
Don’t Spend Your Holiday Season Patching Chrome
9.6 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
NETWORK
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
CHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H
As we come back from our Thanksgiving holidays, Google has released yet another security update for the Chrome desktop web browser to address a high-severity vulnerability that exists in the wild. This is the eighth Chrome zero-day fixed this year by Google. This security bug (CVE-2022-4135; QID 377794) is a Heap buffer overflow in GPU.
Google has withheld details about the vulnerability to prevent expanding its malicious exploitation and to allow users time to apply the security updates necessary on their Chrome installations.
Google’s previous zero-day was also released right before a weekend (see Don’t spend another weekend patching Chrome).

Zero-touch patching of 3rd-party applications
Whether Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari or a host of other 3rd party applications, this is an easy way for bad actors to penetrate your corporate perimeter. And unfortunately, many of these vulnerabilities surface on weekends, and over holiday periods when the majority of IT and Security folks are away from the office and slower to respond.
Remediating 3rd-party applications does not have to be difficult. The risk of patching a desktop application and breaking core business functionality is significantly lower compared to servers running in a production environment. As such applying smart automation to your third-party applications on desktops and laptops will allow organizations to respond faster to new zero-day threats and do it all with little IT intervention or extra work. In other words, once the policy is created, everything else is Zero Touch.
How Qualys Patch Management can help drive speed of remediation
Qualys Patch Management, smart-automation intelligently identifies the riskiest products in the environment and helps create automation jobs to deploy the proper patches and configuration changes required for remediating vulnerabilities, faster than any manual process.
Applications are ranked based on the number of vulnerabilities they introduced to the environment. Common feedback we hear from our customers is that browsers, including Chrome, are in the top five (5) applications that introduced the greatest number of vulnerabilities, and therefore risk. Following the recommendation of this report, it is easy for customers to create automated, zero-touch patch jobs to automatically deploy patches to those top third-party applications. As Qualys supports patching these applications right out of the box, once those jobs are deployed, IT teams and security teams do not need to spend any more time with remediation efforts every time a new patch is released. Aren’t you tired of being a weekend remediation warrior?
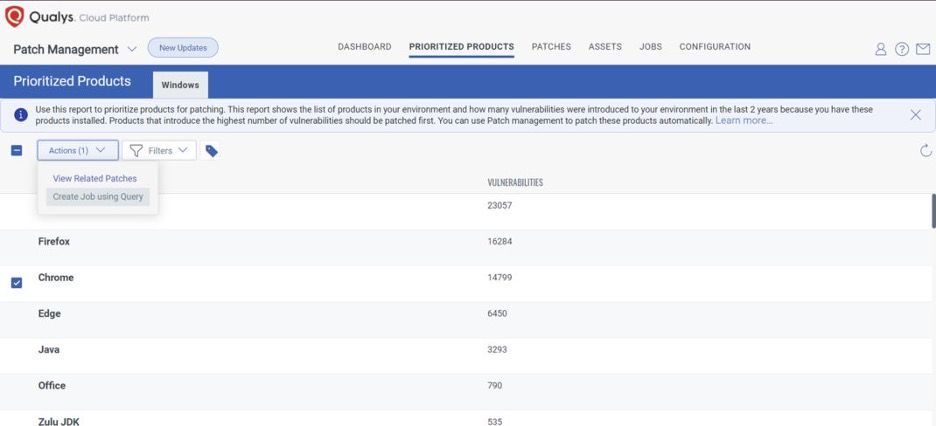
If you are a Qualys customer that does not have Patch enabled, a trial can be enabled quickly – it leverages the same VMDR agent – which will allow you to immediately deploy the Chrome patch to your environment and then create those automation jobs to ensure the next time Google or any other vendor releases a patch, your desktops and laptops are automatically updated.
9.6 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
NETWORK
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
CHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H