
Trellix Global Defenders: Follina — Microsoft Office Zero-Day (CVE-2022-30190)
9.3 High
AI Score
Confidence
Low

Trellix Global Defenders: Follina — Microsoft Office Zero-Day (CVE-2022-30190)
By Taylor Mullins, Robin Noyce,Benjamin Marandel · June 3, 2022
Trellix is continuing to monitor the threat activity associated with the Microsoft Office Zero-Day vulnerability that has been dubbed “Follina.” Chinese-linked Threat Actors are actively exploiting this zero-day vulnerability to execute malicious code remotely. At the time of this writing there is no official patch from Microsoft, but steps and protections can be put into place to mitigate against the attacks utilizing this Microsoft vulnerability.
Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The method at which these attacks are taking place is using malicious Word documents that execute PowerShell commands via the Microsoft Diagnostic Tool (MSDT). The ‘Follina’ zero-day features a remote code execution that works without elevated privileges, does not require macro enablement to execute binaries or scripts, and can bypass Windows Defender detection. Opening a Microsoft Word document in preview mode in Explorer is another method to detonate the malicious code which provides a vector for the exploitation to take place outside of the Protected View that Microsoft is reporting will prevent the attack. Furthermore, it is a signed binary, which enables the code to bypass windows validation controls. The Follina vulnerability is exploitable with Office 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, Office ProPlus and Office 365.
Microsoft recommended workaround for microsoft support diagnostic tool (MSDT)
Microsoft has released guidance on disabling the Microsoft Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) URL protocol. The Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) is a tool designed to collect information to send to the Microsoft Support.
CISA: Microsoft Releases Workaround Guidance for MSDT “Follina” Vulnerability
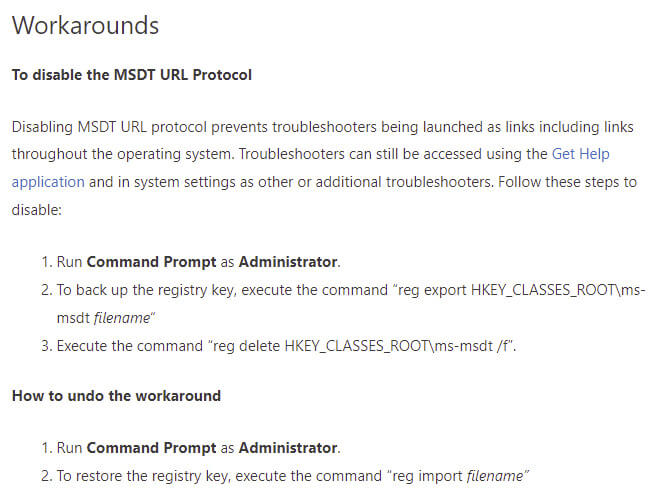 Figure 1. Workaround provided by Microsoft to mitigate against exploitation
Figure 1. Workaround provided by Microsoft to mitigate against exploitation
Trellix product protections for follina vulnerability
Trellix is continuing to add protections via threat feeds and content updates to the Trellix products as Indicators of Compromises (IOCs) and behavioral techniques are detected in the wild. In addition, there are initiative-taking steps that can further protect your environment against the attacks targeting the Follina zero-day vulnerability.
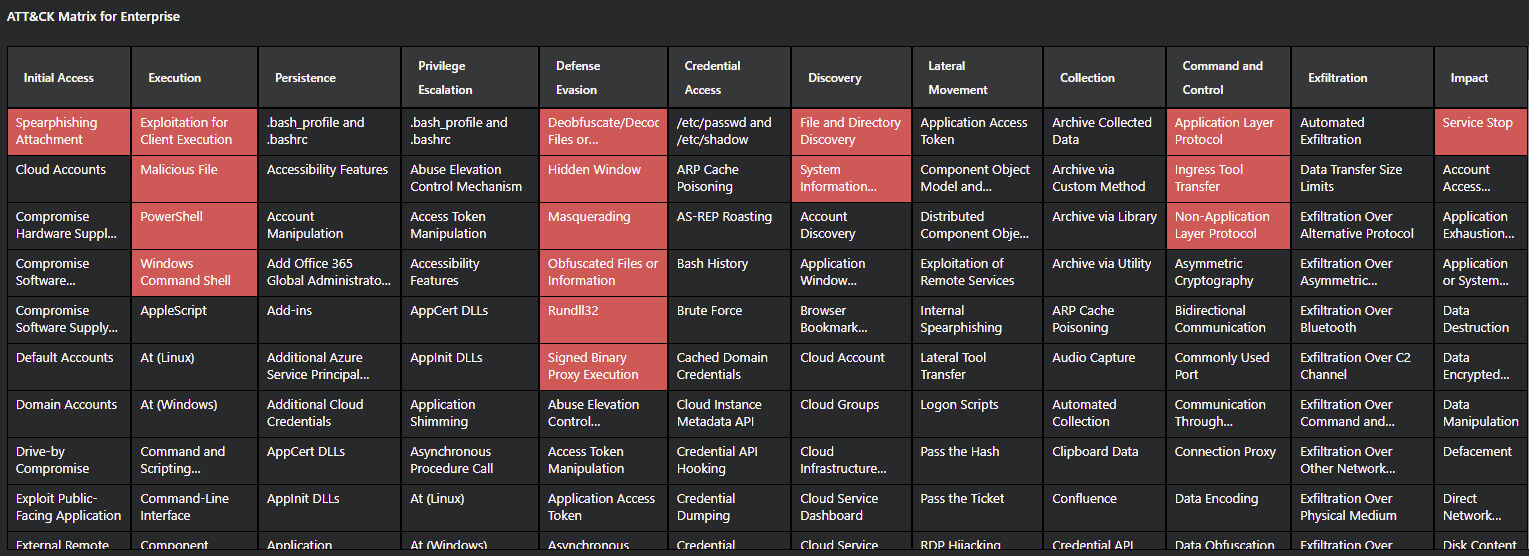 Figure 2. MITRE ATT&CK Matrix for Exploitation of Follina Vulnerability. Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 2. MITRE ATT&CK Matrix for Exploitation of Follina Vulnerability. Source: MVISION Insights
Follina zero-day threat intelligence and hunting rules
MVISION Insights is continually updated with the latest threat intelligence and known indicators that are being discovered related to the Microsoft zero-day vulnerability. Additionally, applying hunting rules and threat intelligence across the security stack is key for early detection and identification of the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) associated with Follina.
MVISION Insights Campaign Name - Follina — A Microsoft Office Code Execution Vulnerability
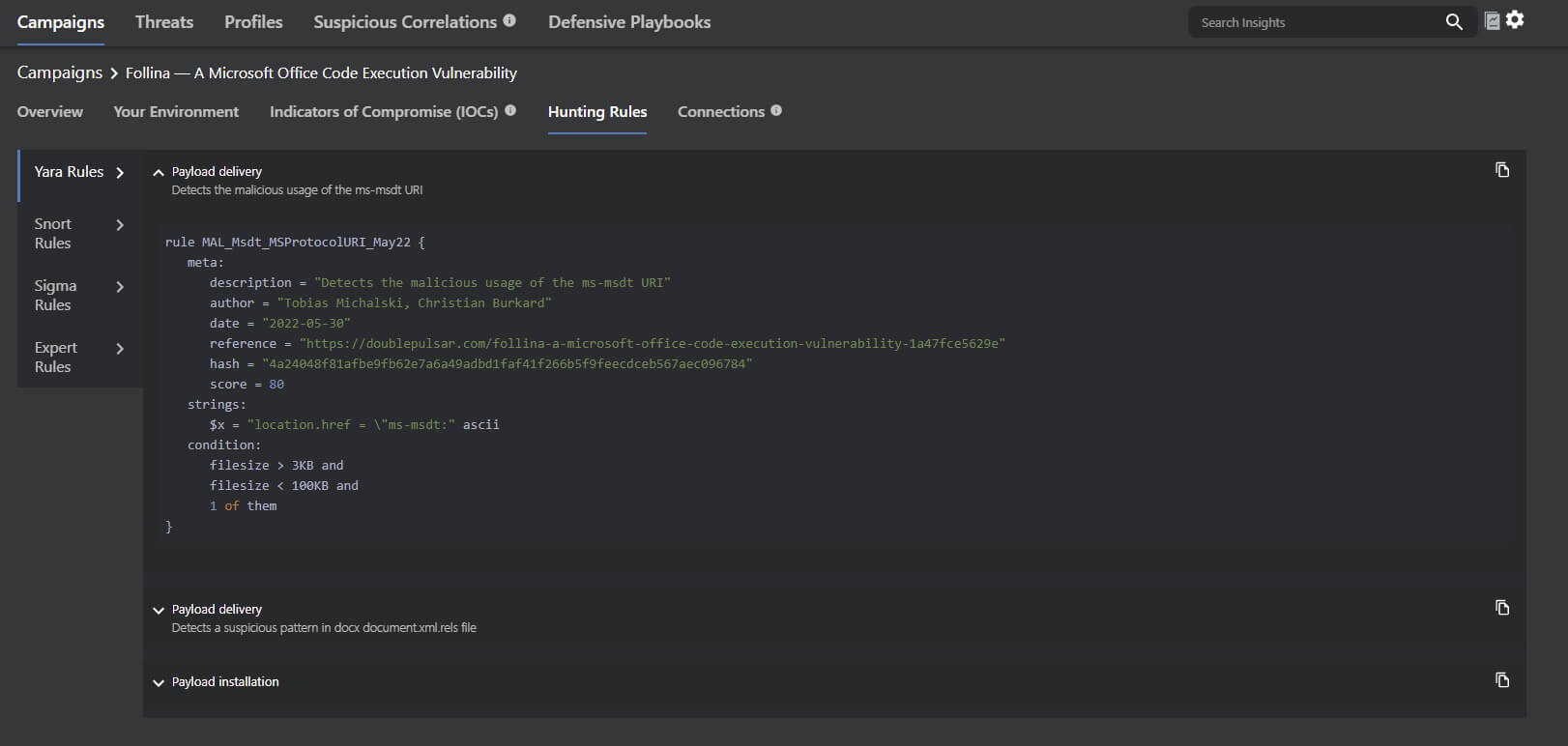 Figure 3. YARA, Snort, and Sigma Hunting Rules specific to Follina Vulnerability Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 3. YARA, Snort, and Sigma Hunting Rules specific to Follina Vulnerability Source: MVISION Insights
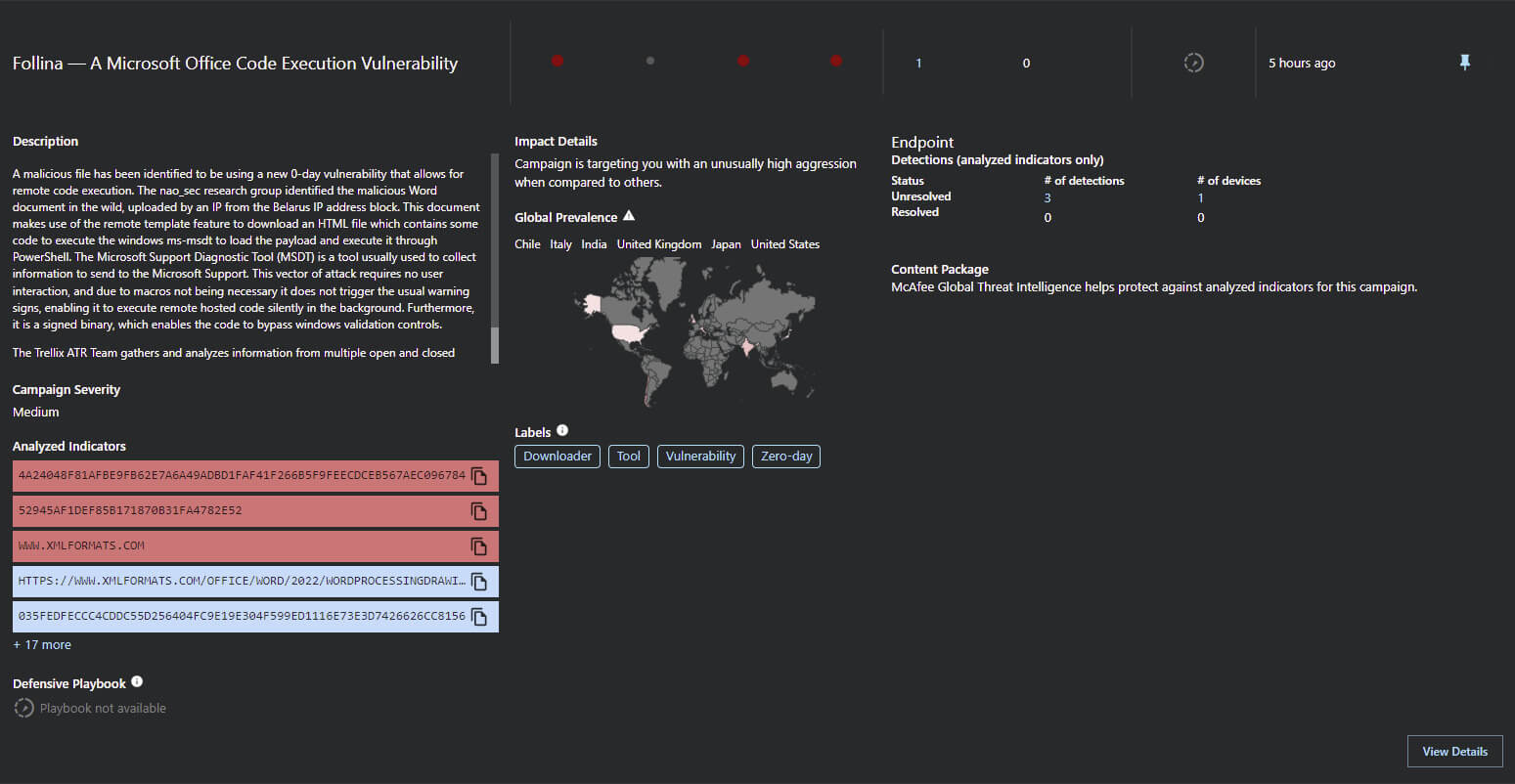 Figure 4. Campaign overview and detections for Follina. Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 4. Campaign overview and detections for Follina. Source: MVISION Insights
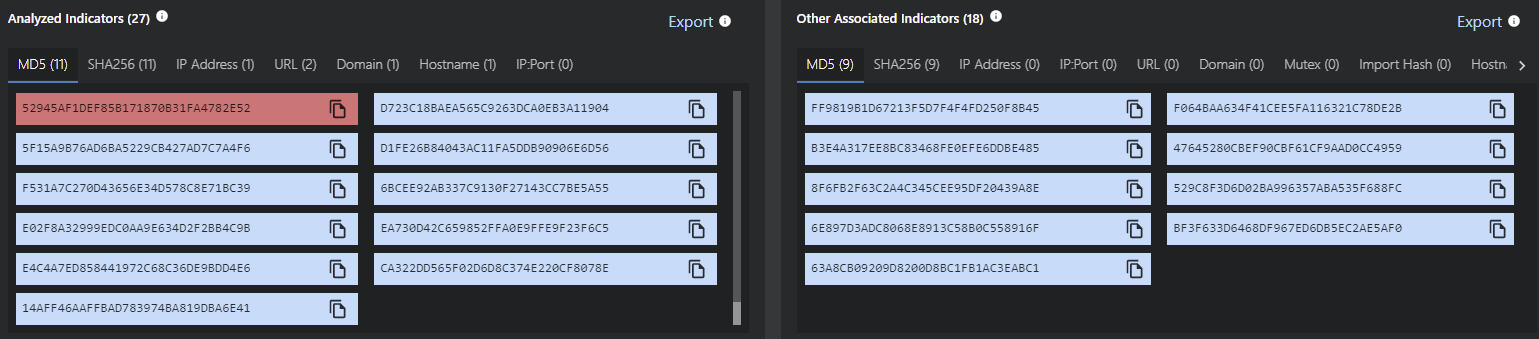 Figure 5. Follina Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and endpoint detections. Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 5. Follina Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and endpoint detections. Source: MVISION Insights
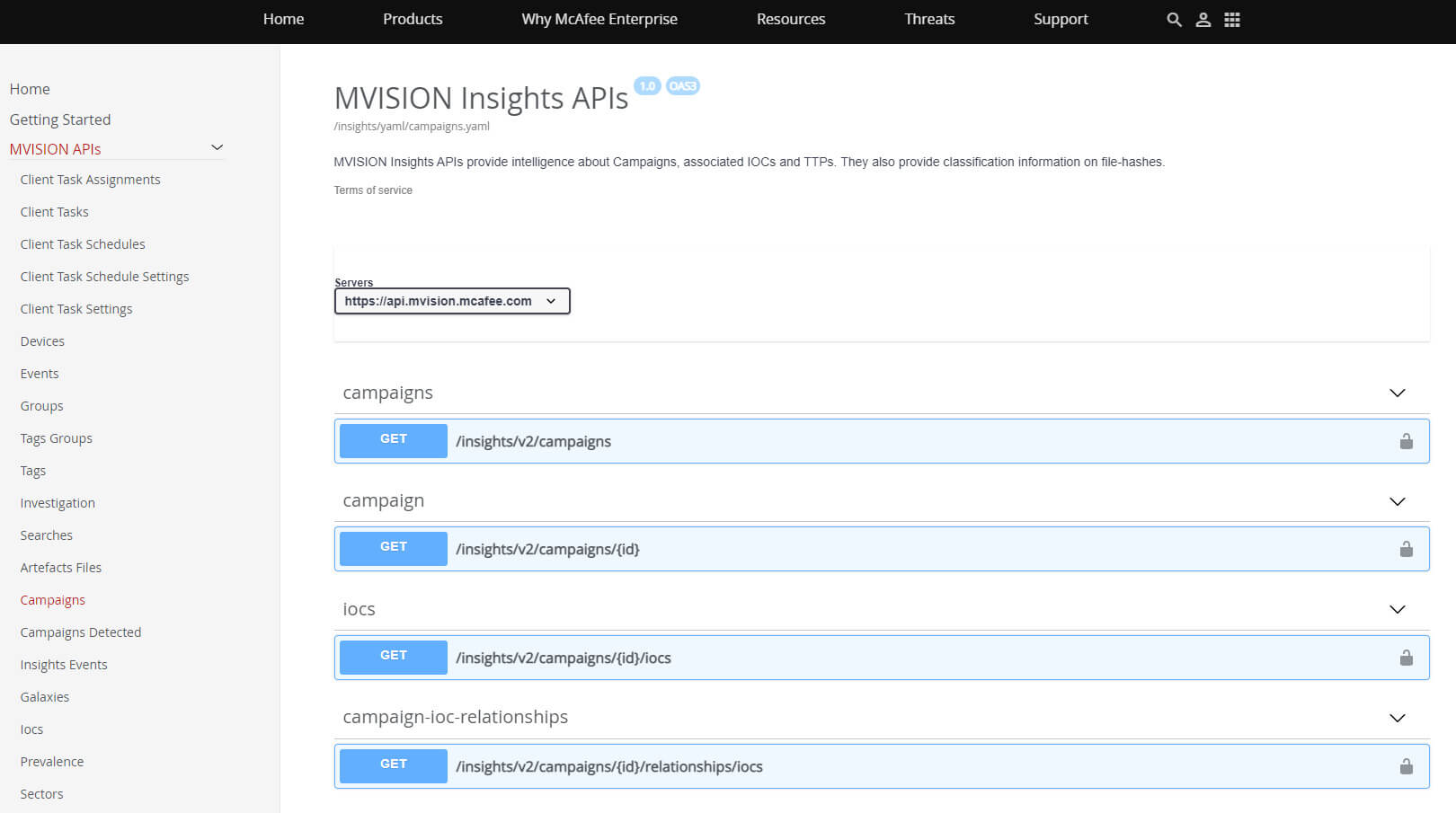 Figure 6. MVISION Insights API to pull Campaign Threat Intelligence for further correlation across data events.
Figure 6. MVISION Insights API to pull Campaign Threat Intelligence for further correlation across data events.
Utilizing expert and behavioral rules in trellix endpoint security
Trellix ENS Threat Prevention and Adaptive Threat Protection (ATP) monitor Microsoft Word process activity and the start of a child Command line processes is detected and blocked (if configured to) by ENS ATP. Trellix ENS can also block common processes like cmd.exe from being spawned by Microsoft Office applications in a suspicious manner. The following rules in Trellix ENS Exploit Prevention and Adaptive Threat Protection (ATP) are recommended to observe or block behavioral activity associated with exploitation techniques.
Exploit Prevention Signature 6113: T1055 - Fileless Threat: Reflective Self Injection
Exploit Prevention Signature 6127: Suspicious LSASS Access from PowerShell
Exploit Prevention Signature 6143: T1003 - Attempt to Dump Password Hash from SAM Database
Exploit Prevention Signature 8004: Fileless Threat: Malicious PowerShell Behavior Detected
ATP Rule 239: Identify suspicious command parameter execution
ATP Rule 263: Detect processes accessing suspicious URLs
ATP Rule 301: Blocks cmd.exe from being spawned by office applications
ATP Rule 332: Prevent certutil.exe from downloading or decoding files with suspect extensions
The Trellix Advanced Threat Research (ATR) team has also created the following ENS Expert Rule to prevent techniques associated with exploitation. Outlined below are several screenshots on how to create this specific Expert Rule in Trellix ENS. Per standard practice, we recommend that customers test this rule in Report Only before moving to Block mode.
Detect new code injection method in Microsoft Office CVE-2022-30190
How to Use Expert Rules in ENS to Prevent Malicious Exploits
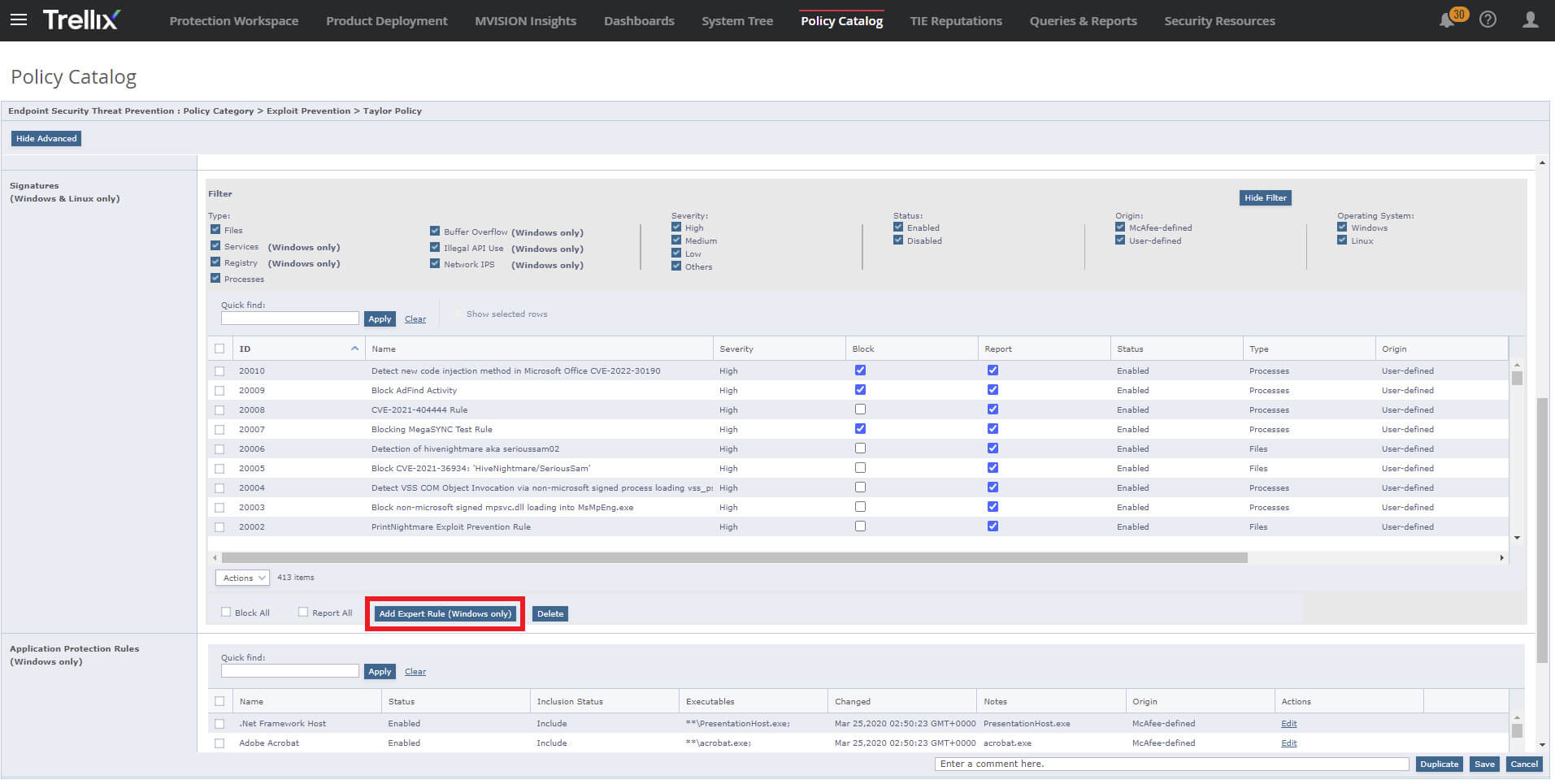 Figure 7. Creation of the Expert Rule in the Trellix ENS Exploit Prevention Policy
Figure 7. Creation of the Expert Rule in the Trellix ENS Exploit Prevention Policy
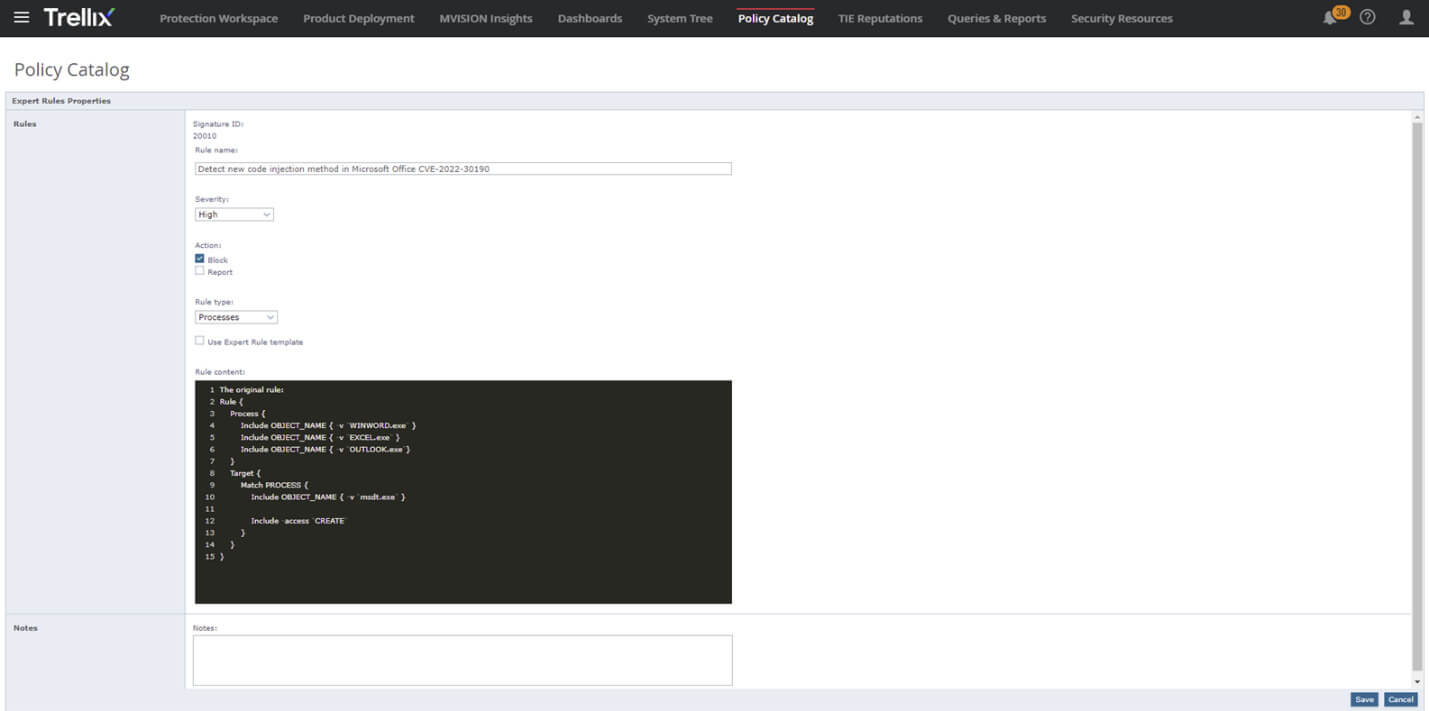 Figure 8. Creating specific Expert Rule for Microsoft Office (CVE-2022-30190) in Trellix ENS
Figure 8. Creating specific Expert Rule for Microsoft Office (CVE-2022-30190) in Trellix ENS
Hunting for suspicious behavior with MVISION EDR
MVISION EDR has the capability to search across historical and real-time data on endpoints to identify specific activity associated with exploitation and the MSDT process. Several examples and queries are noted below for using Historical and Real-time searches to analyze the Microsoft Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) process activity and interaction with CMD and PowerShell.
Processes and HostInfo hostname where Processes name equals msdt.exe – Real-time search query to locate activity specific to the Microsoft Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) process
ProcessName = msdt.exe – Historical search string to locate prior activity from MSDT.exe across your endpoints even if they are currently offline.
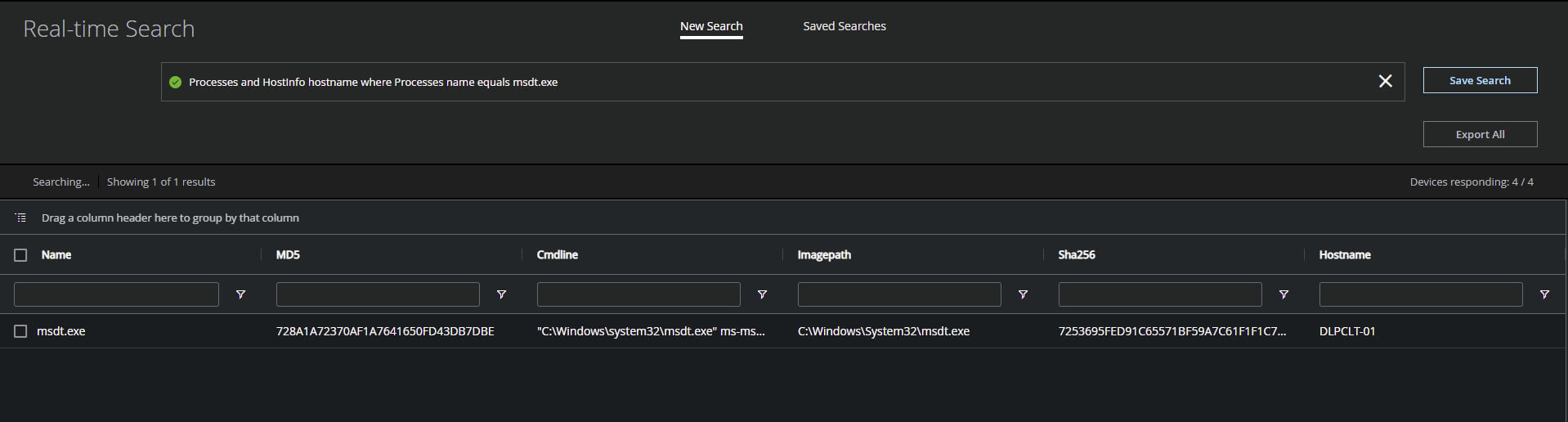 Figure 9. MVISION EDR Real-time search to locate ongoing MSDT.exe activity
Figure 9. MVISION EDR Real-time search to locate ongoing MSDT.exe activity
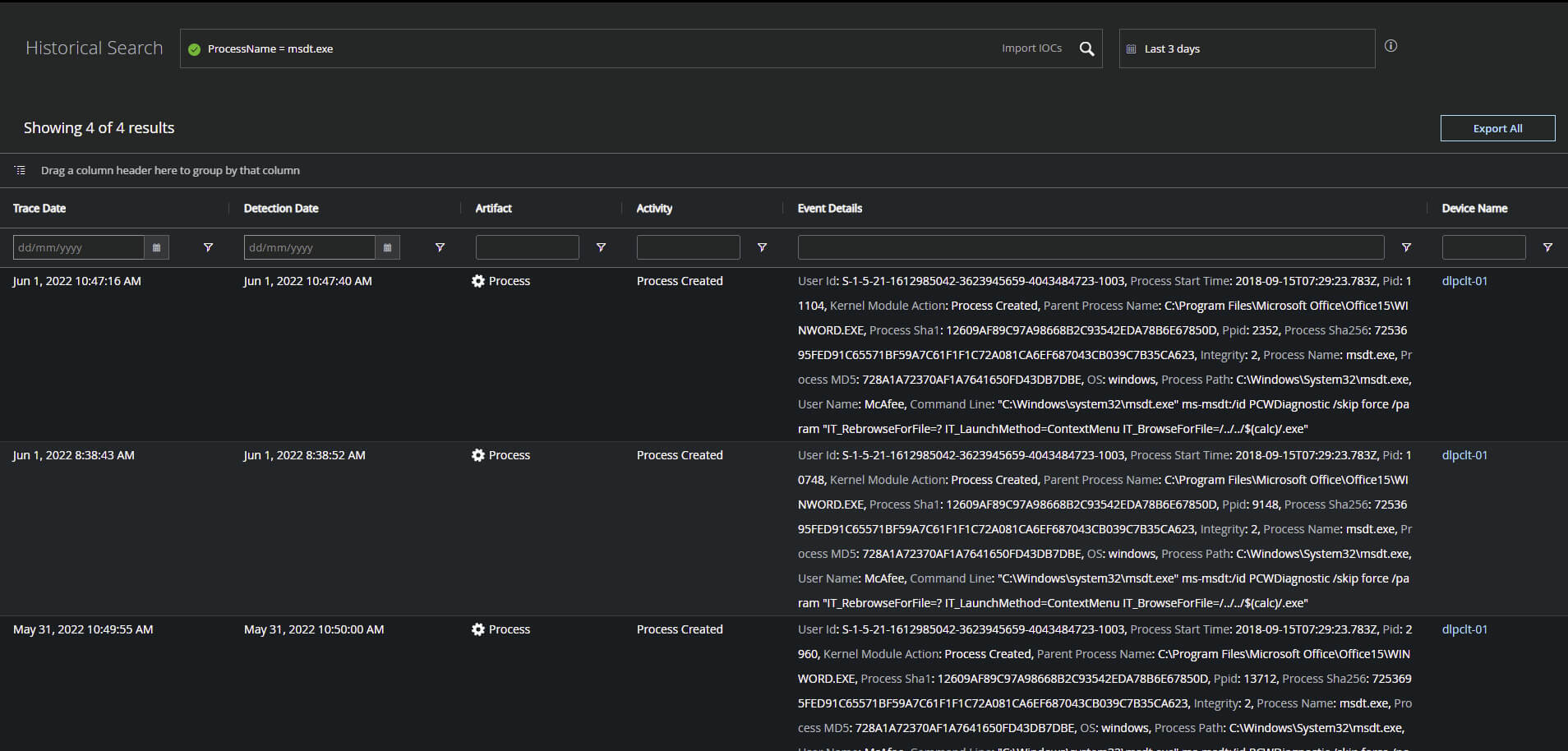 Figure 10. MVISION EDR Historical Search query across all endpoints either online or offline to locate prior MSDT.exe process activity
Figure 10. MVISION EDR Historical Search query across all endpoints either online or offline to locate prior MSDT.exe process activity
Trellix network security platform signature release
Trellix has released a User-Defined Signature (UDS) for the Network Security Platform (NSP) to provide an immediate solution to this security advisory. Trellix writes and tests these signatures with the objective of a quick turnaround.
Additional resources
Microsoft: Guidance for CVE-2022-30190 Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool Vulnerability
Huntress: Rapid Response: Microsoft Office RCE - “Follina” MSDT Attack
Bleeping Computer: Windows MSDT zero-day now exploited by Chinese APT hackers