
Analysis and Protections for RagnarLocker Ransomware

Trellix Global Defenders: Analysis and Protections for RagnarLocker Ransomware
By Taylor Mullins · February 28, 2022
The United States Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) has released a Flash Alert warning that the RagnarLocker ransomware gang has breached the networks of at least fifty-two organizations from multiple critical infrastructure sectors across the United States. This is the second FBI alert released for the RagnarLocker Ransomware variant, the last alert was released in November 2020.
The following FBI flash alerts will focus on providing indicators of compromise (IOCs) that organizations can use to detect and block RagnarLocker ransomware attacks.
March 2022 FBI Alert (PDF) - RagnarLocker Ransomware Indicators of Compromise
November 2020 FBI Alert (PDF) - RagnarLocker Ransomware Indicators of Compromise
RagnarLocker ransomware first appeared in the wild at the end of December 2019 as part of a campaign against compromised networks targeted by its operators. The actors behind RagnarLocker will perform reconnaissance on the targeted network, exfiltrate sensitive information, encrypt files, and then notify the victim the stolen files will be released to the public if the ransom is not paid. The threat actor behind the malware is known in previous attacks to ask for millions of dollars in payment and creates a ransom note that includes the company name. The ransomware enumerates all running services on the infected host and stops services that contain a specific string. Ragnar is small compared to other malware and is written in the C/C++ programming language.
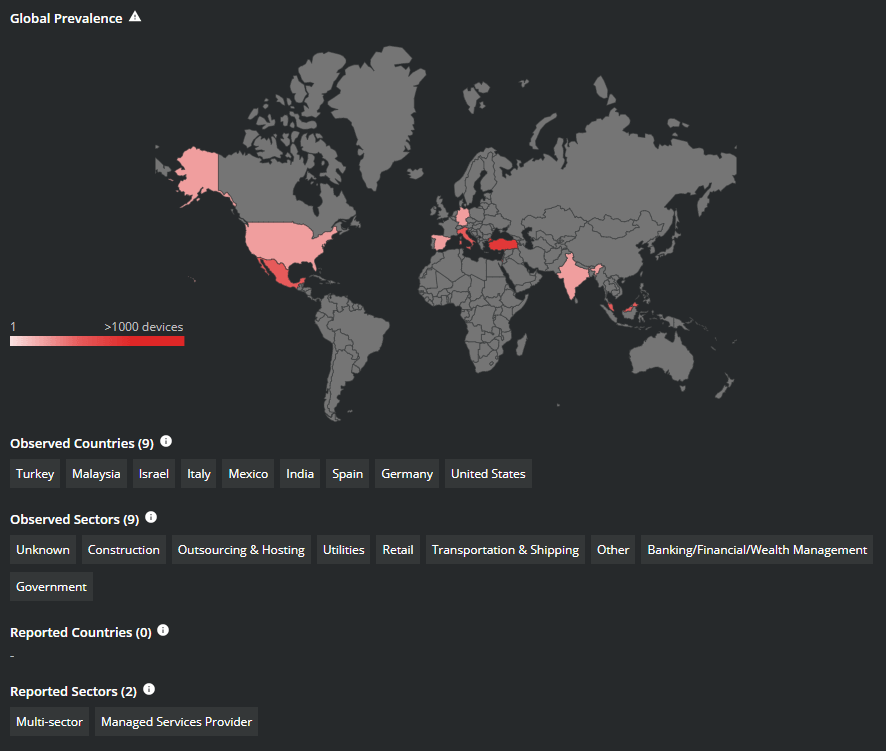 Figure 1. Global Detections and Observed Sectors for RagnarLocker Ransomware. Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 1. Global Detections and Observed Sectors for RagnarLocker Ransomware. Source: MVISION Insights 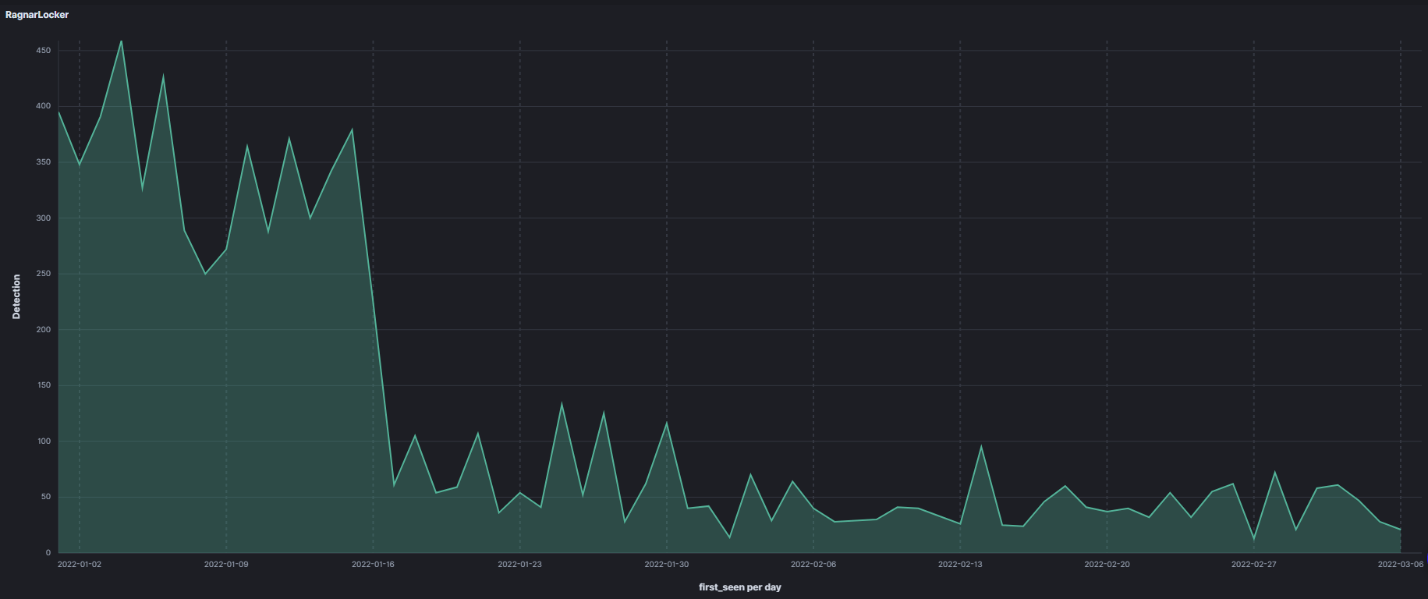 Figure 2. Last 60 days of detections for RagnarLocker Ransomware. Source: Trellix APG Team
Figure 2. Last 60 days of detections for RagnarLocker Ransomware. Source: Trellix APG Team
Recommended Steps to Prevent Initial Access
The threat actors behind the RagnarLocker attacks often gain entry by compromising the company’s network via the RDP service, using brute force attacks to guess weak passwords or with stolen credentials purchased on the Dark Web.
- Disable unused remote access/Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) ports and monitor remote access/RDP logs for any unusual activity.
- After gaining access the exploitation of CVE-2017-0213 is used to elevate privileges, patching of this CVE is critical.
- Reviewing the CVEs for all Public Facing Systems – CISA regularly updates and maintains a full list of CVEs that are known to be exploited: CISA: KNOWN EXPLOITED VULNERABILITIES CATALOG
- Over 90% of successful cyber-attacks begin with a phishing email and has been a technique used by RagnarLocker, it is critical to continually monitor for spearphishing campaigns with malicious attachments and links.
- Communication – Along with monitoring, educating end users on what they could be receiving in their email can help them spot phishing campaigns before they click or download.
- Review Indicators of Compromise in FBI alerts and block the malicious IP addresses observed in previous attacks.
Trellix Protections and Global Detections
Trellix Global Threat Intelligence (GTI) is currently detecting all known analyzed indicators for this campaign across their products that use the GTI threat feed.
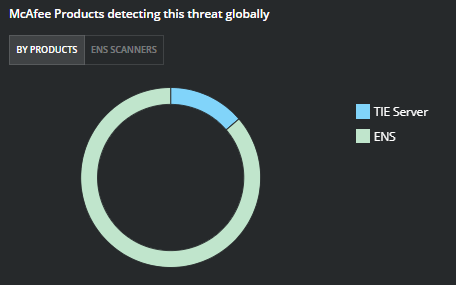 Figure 3. Trellix Products detecting this threat globally. Source: MVISION Insights
Figure 3. Trellix Products detecting this threat globally. Source: MVISION Insights
Blocking RagnarLocker Attacks with Endpoint Security
Trellix ENS is currently detecting RagnarLocker Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) with signature detections and the malware behavior associated with RagnarLocker Ransomware attacks. The following Adaptive Threat Protection Rules in ENS have shown success in stopping the techniques associated with RagnarLocker. Trellix always recommends testing in Report Only Mode before blocking to confirm no false positives are detected by this behavioral rule.
Coverage
Minimum AMCore Content: 4217
Adaptive Threat Protection Rule ID 239: Identify suspicious command parameter execution (Mitre-T1059: Identifies the suspicious execution of an application through command line parameters).
Adaptive Threat Protection Rule ID 341: Identify and block patterns being used in Ransomware attacks in security rule group assignments.
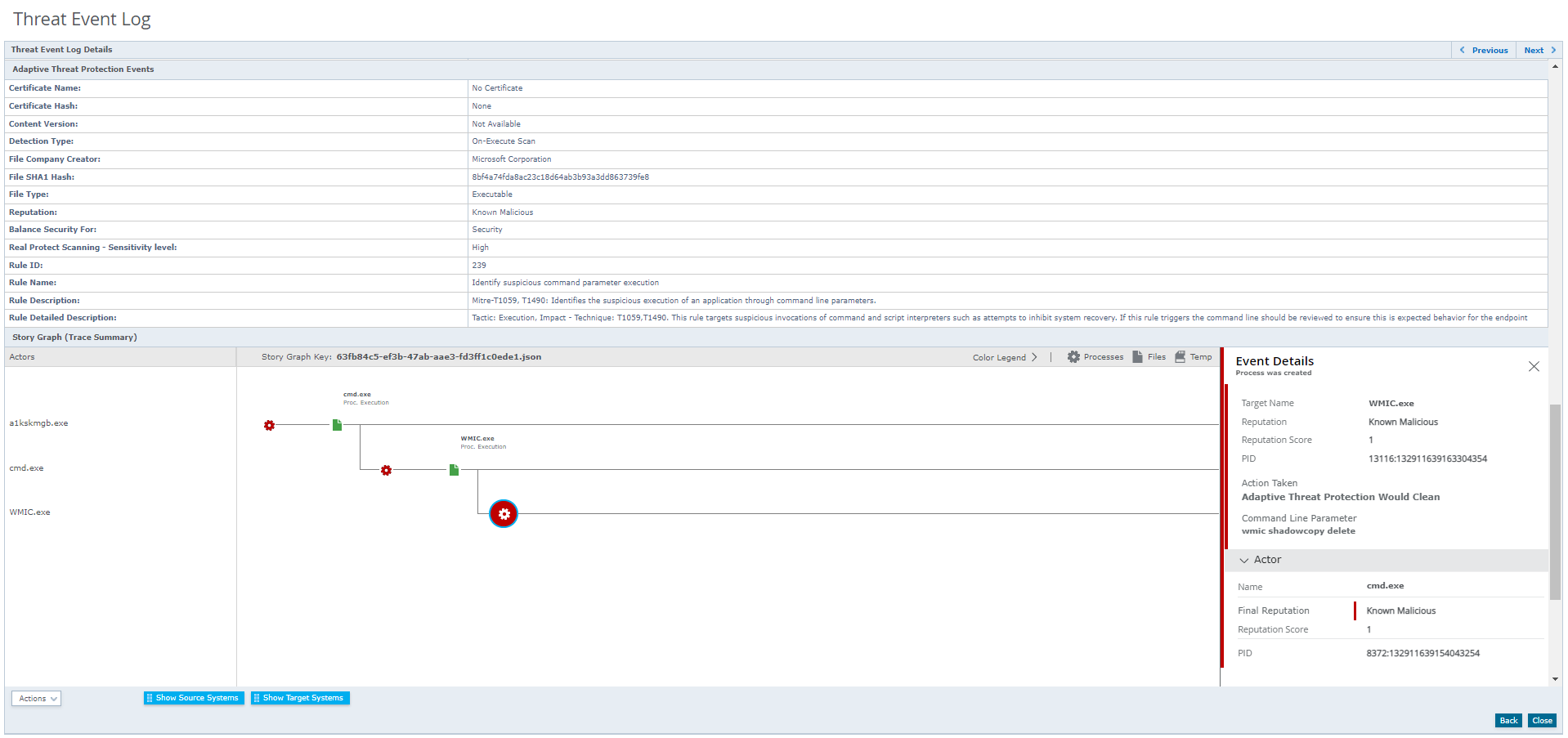 Figure 4. Story Graph and Adaptive Threat Protection Detection for Rule ID 239 in ePolicy Orchestrator/MVISION ePO
Figure 4. Story Graph and Adaptive Threat Protection Detection for Rule ID 239 in ePolicy Orchestrator/MVISION ePO 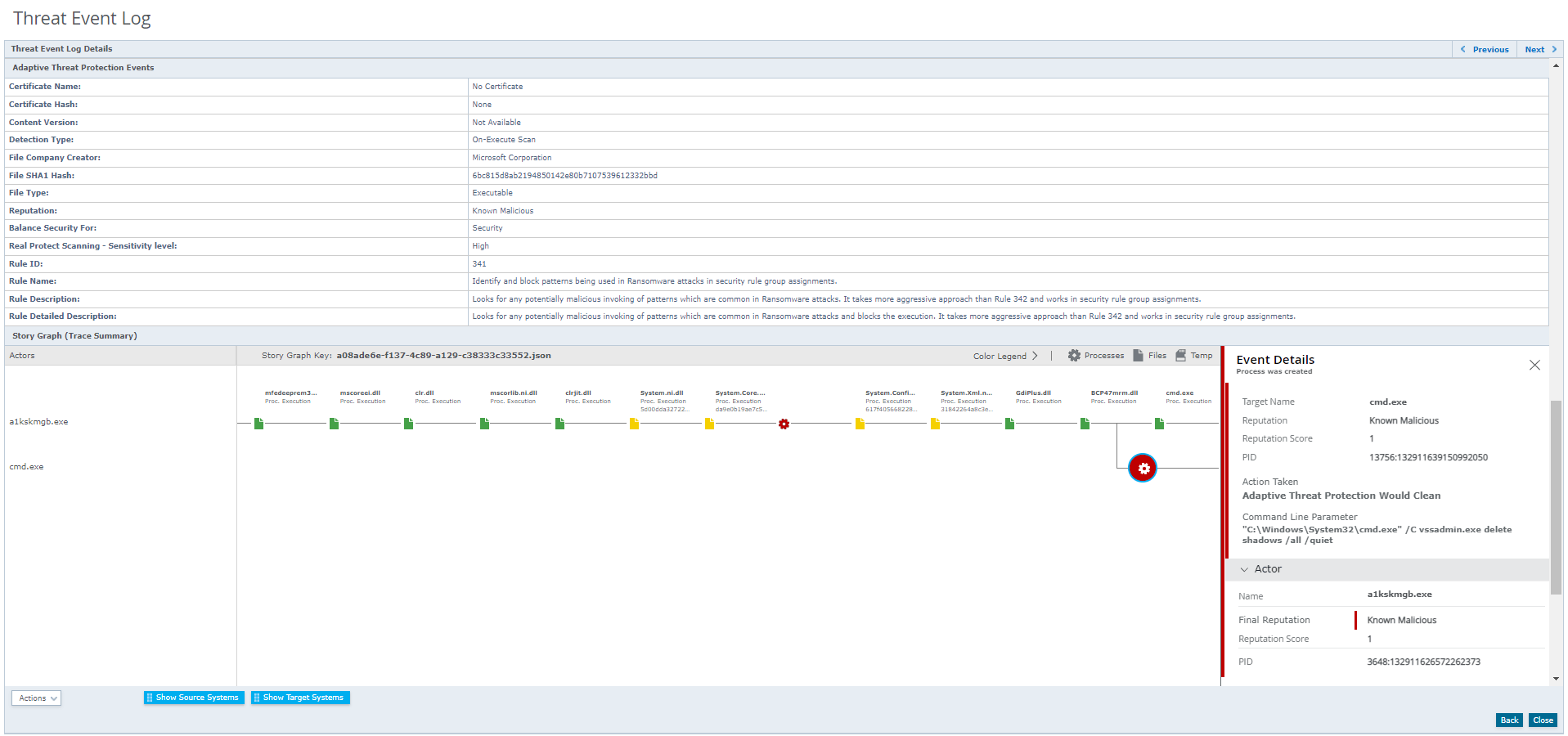 Figure 5. Story Graph and Adaptive Threat Protection Detection for Rule ID 341 in ePolicy Orchestrator/MVISION ePO
Figure 5. Story Graph and Adaptive Threat Protection Detection for Rule ID 341 in ePolicy Orchestrator/MVISION ePO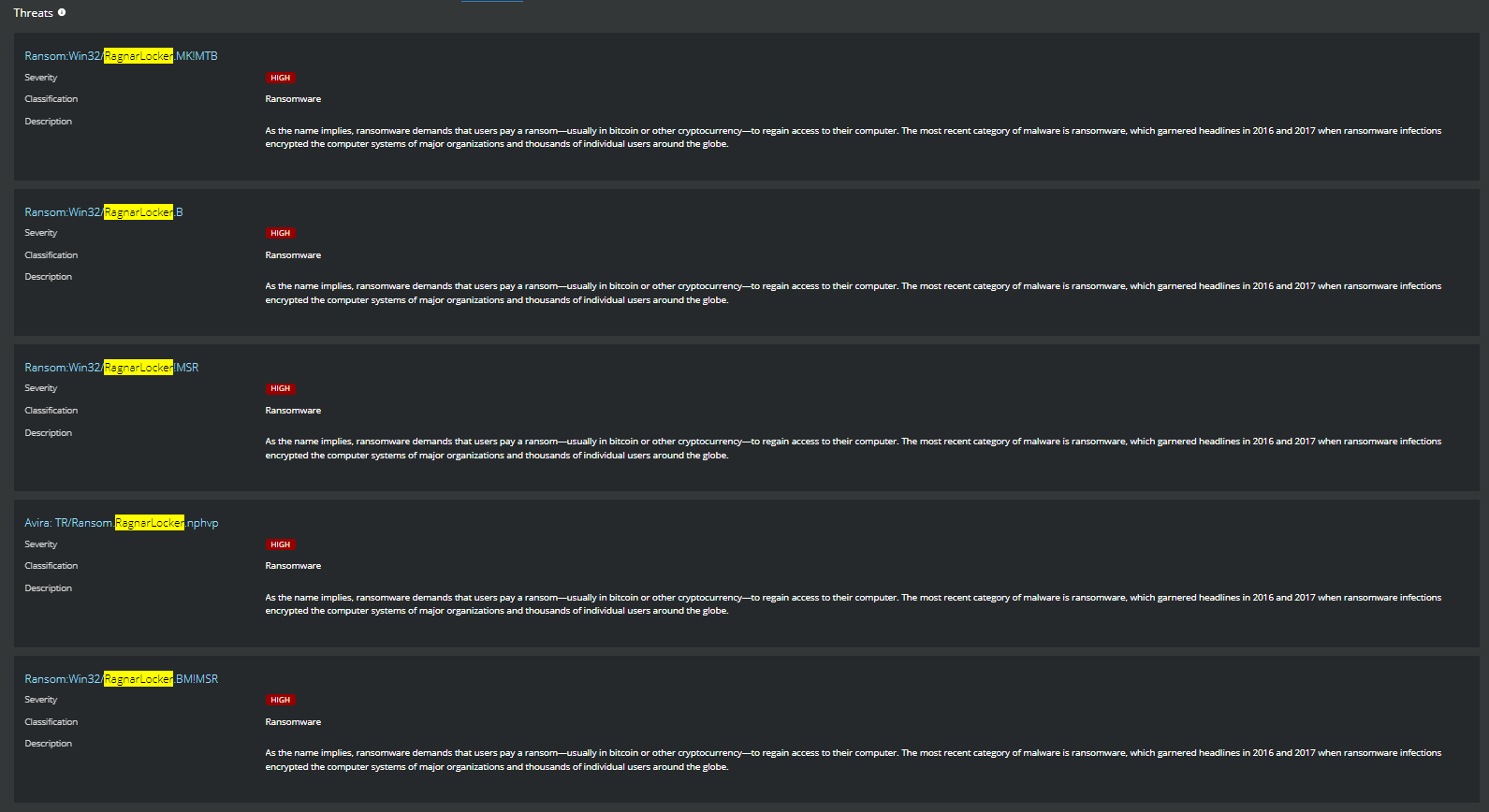 Figure 6. Threat detections for RagnarLocker Ransomware shown in MVISION Insights
Figure 6. Threat detections for RagnarLocker Ransomware shown in MVISION Insights
RagnarLocker Threat Intelligence from the Trellix Advanced Threat Research Team and MVISION Insights
MVISION Insights will provide the current threat intelligence and known indicators for RagnarLocker Ransomware. MVISION Insights will alert to detections and Process Traces that have been observed and systems that require additional attention to prevent widespread infection. MVISION Insights will also include Hunting Rules for threat hunting and further intelligence gathering of the threat activity and adversary.
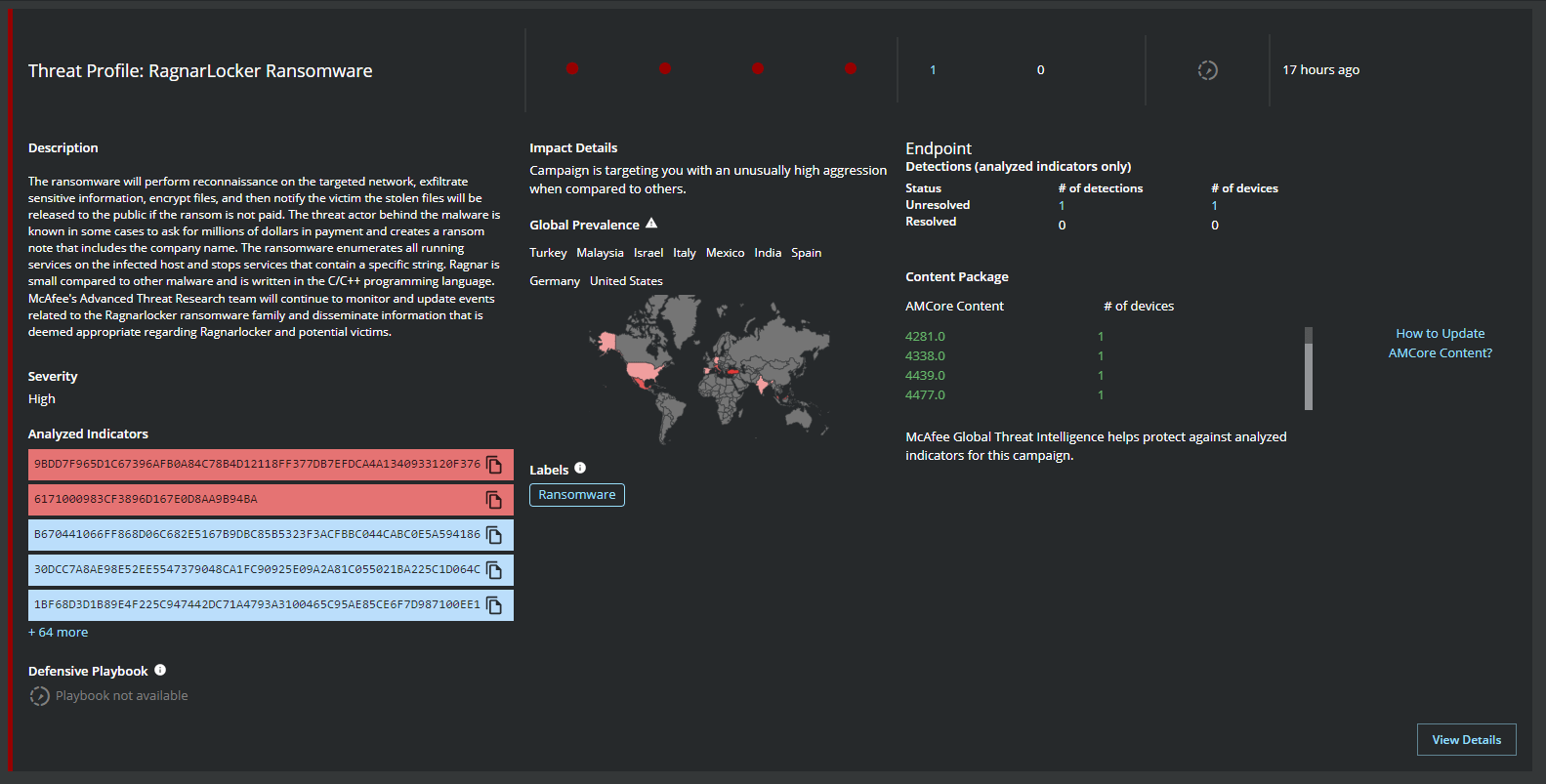 Figure 7. Campaign Details, Analyzed Indicators of Compromise, and Detections
Figure 7. Campaign Details, Analyzed Indicators of Compromise, and Detections 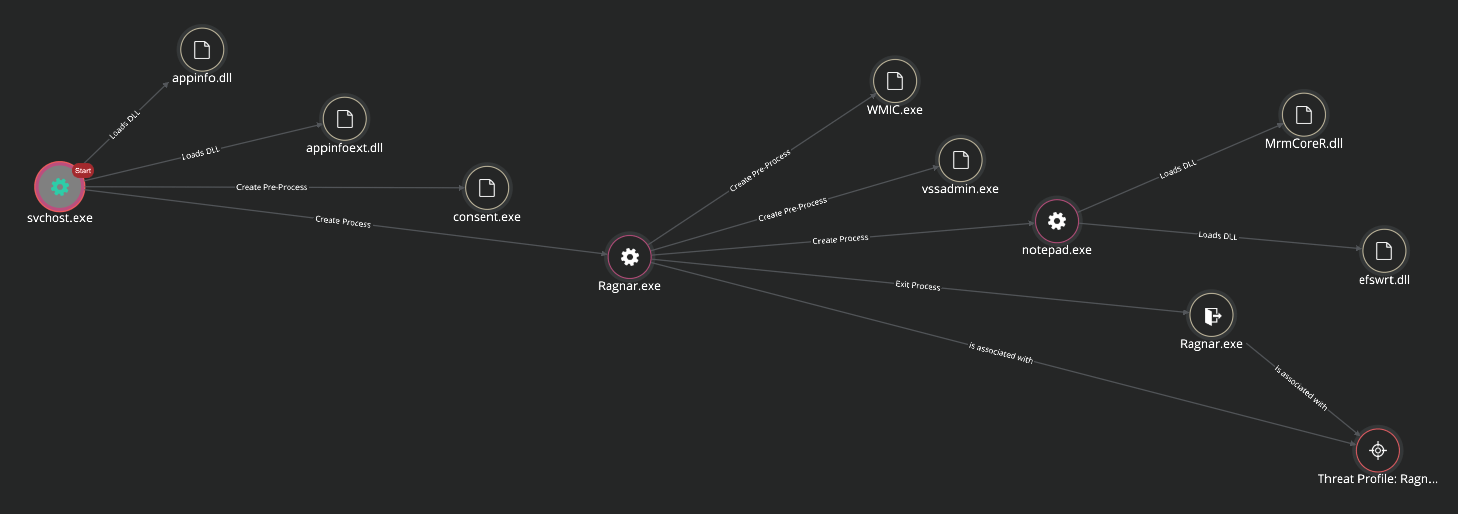 Figure 8. Process Trace for RagnarLocker Ransomware activity in MVISION Insights
Figure 8. Process Trace for RagnarLocker Ransomware activity in MVISION Insights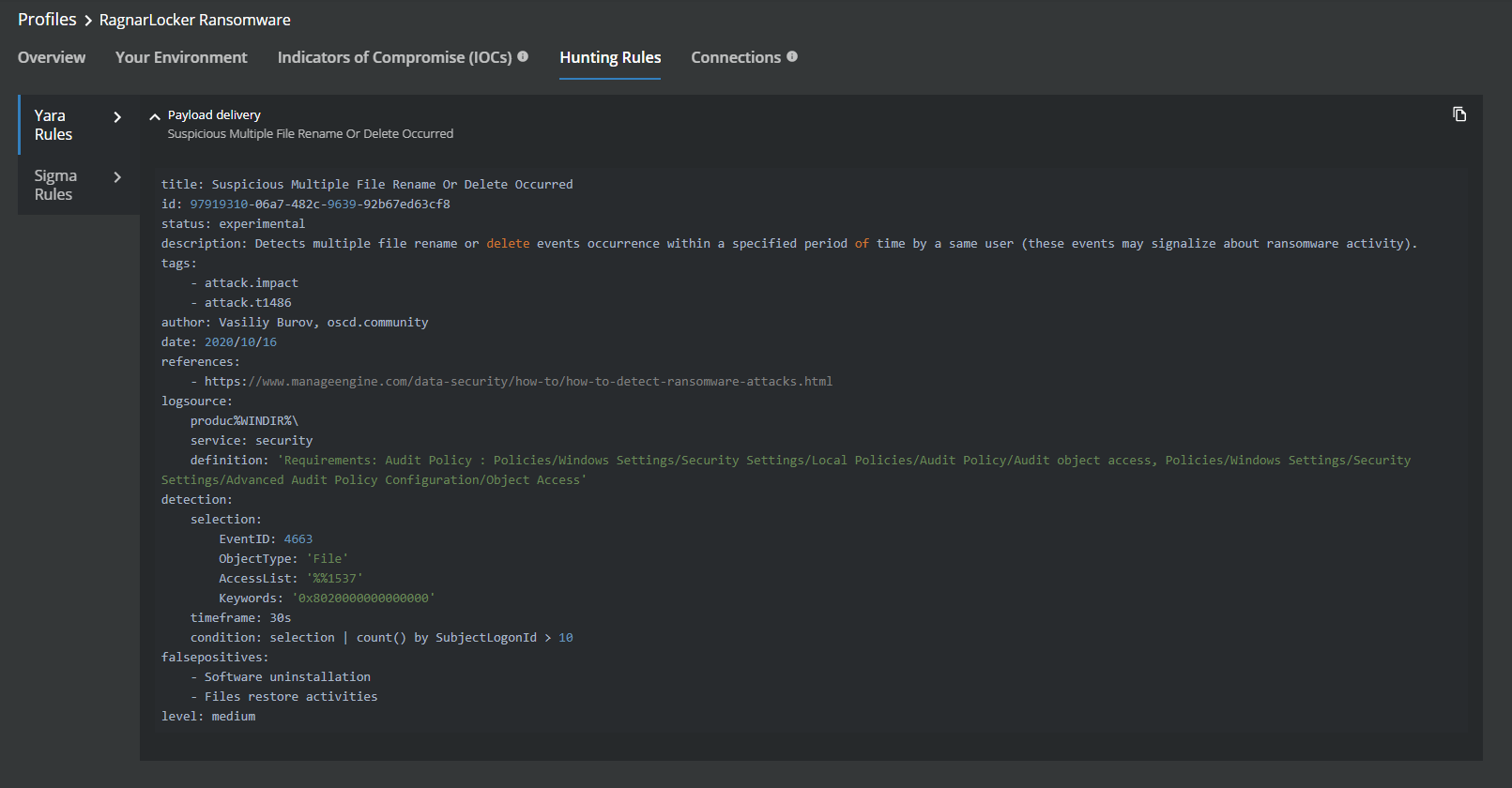 Figure 9. Hunting Rules for RagnarLocker Ransomware in MVISION Insights
Figure 9. Hunting Rules for RagnarLocker Ransomware in MVISION Insights
Detecting Malicious Activity with MVISION EDR
MVISION EDR is currently monitoring for the activity associated with RagnarLocker Ransomware and will note the MITRE techniques and any suspicious indicators related to the adversarial activity. Analysis of RagnarLocker malware samples note the usage of native Windows APIs, Microsoft Connection Manager Profile Installer (CMSTP.exe), and the deletion of Shadow Copy to inhibit system recovery.
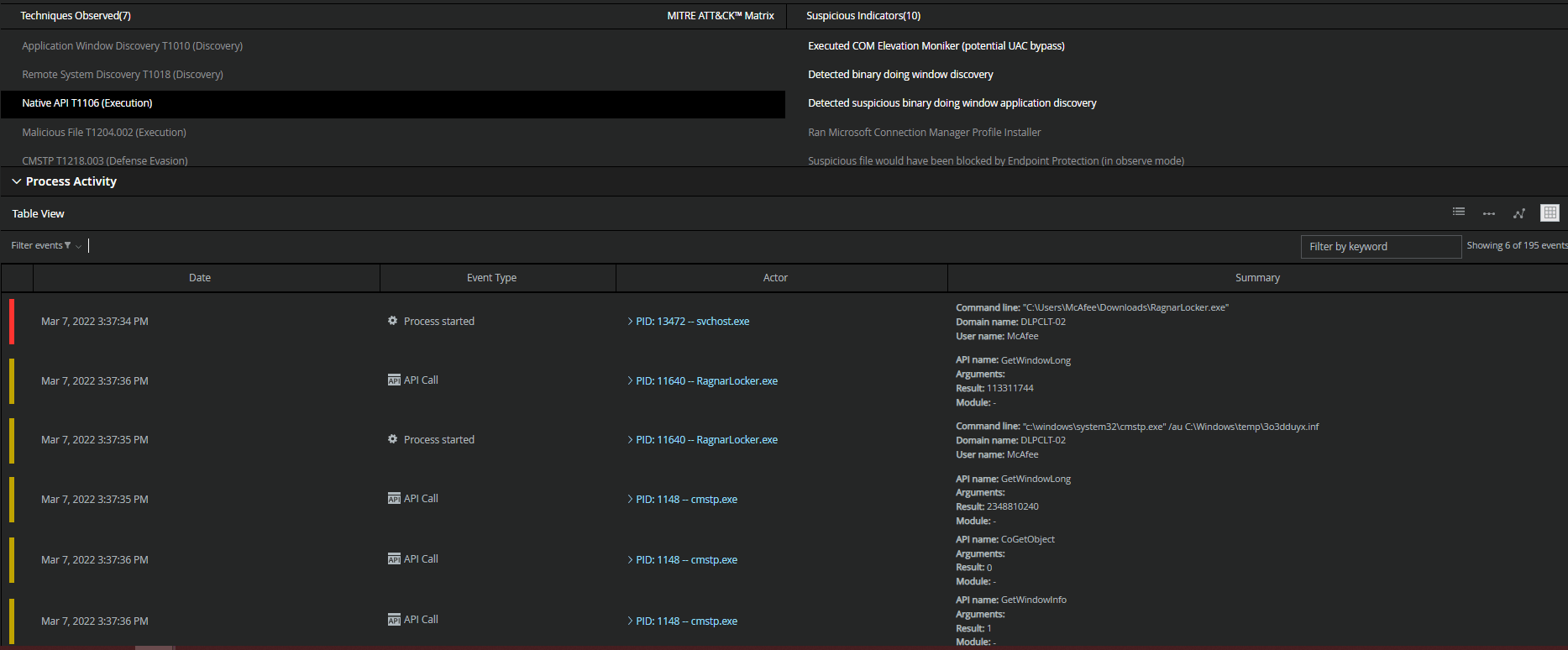 Figure 10. Interaction with the native OS application programming interface (API) to execute behaviors.
Figure 10. Interaction with the native OS application programming interface (API) to execute behaviors. 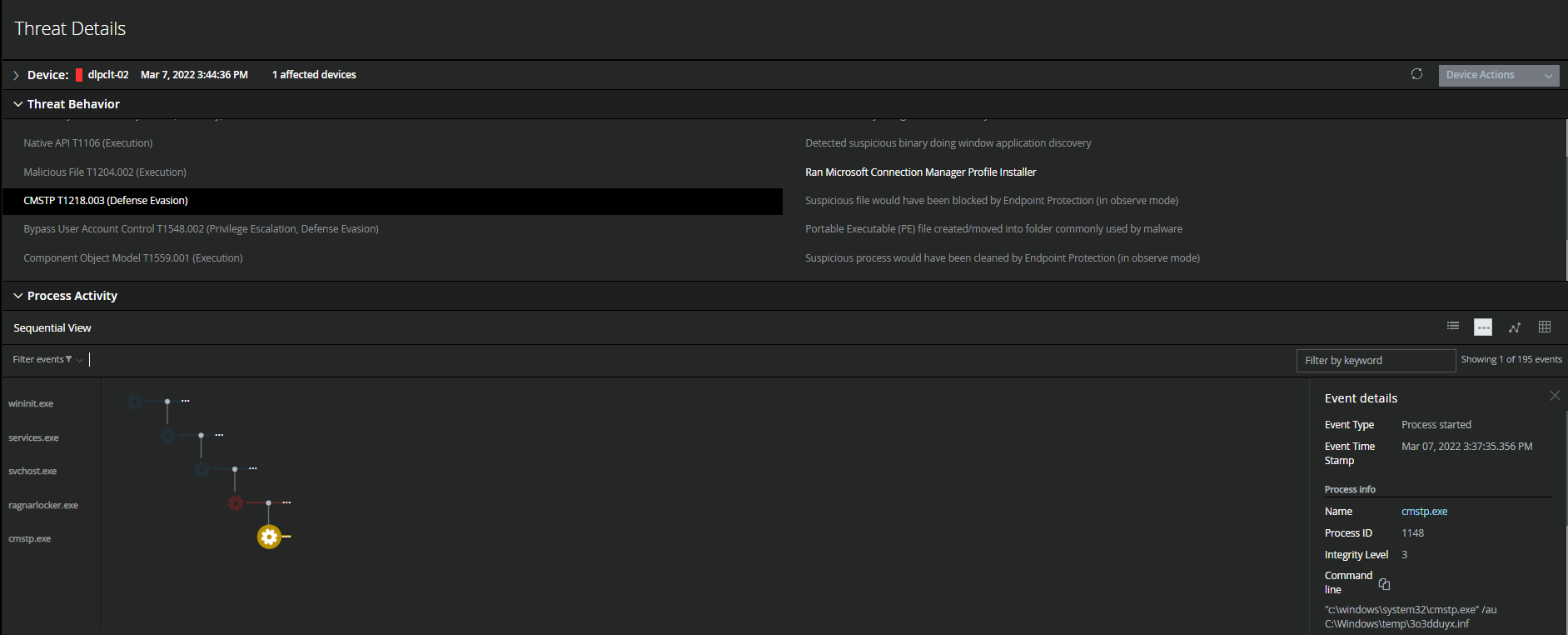 **Figure 11. T1218.003 – Adversaries may abuse CMSTP to proxy execution of malicious code. **The Microsoft Connection Manager Profile Installer (CMSTP.exe) is a command-line program used to install Connection Manager service profiles.
**Figure 11. T1218.003 – Adversaries may abuse CMSTP to proxy execution of malicious code. **The Microsoft Connection Manager Profile Installer (CMSTP.exe) is a command-line program used to install Connection Manager service profiles. 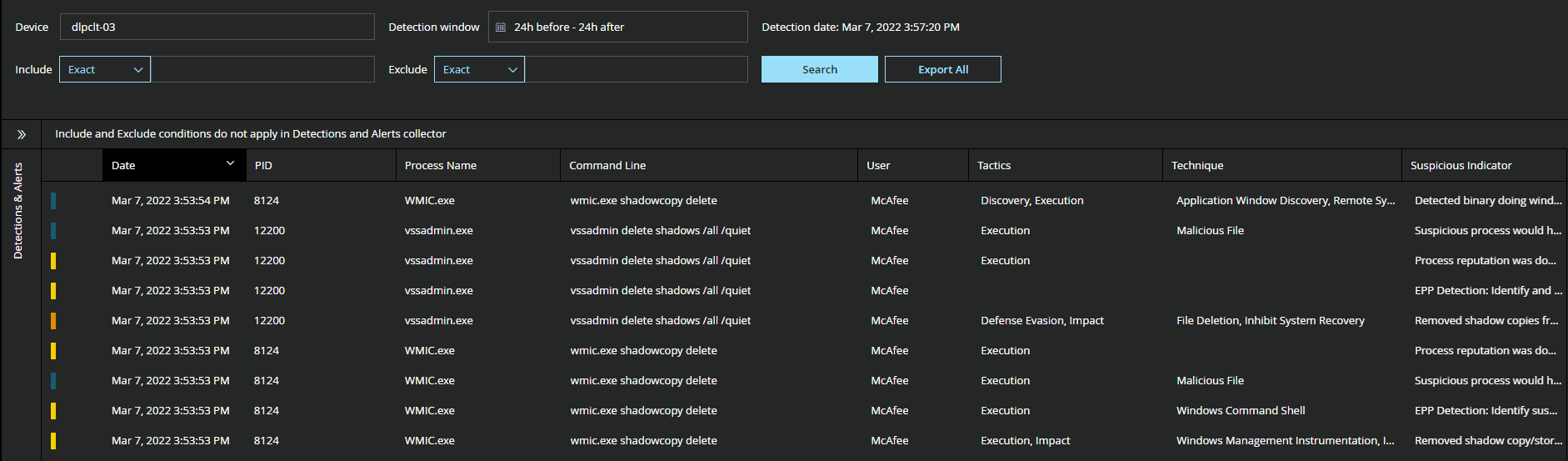 Figure 12. Native Windows utilities utilized by adversaries to disable or delete system recovery.
Figure 12. Native Windows utilities utilized by adversaries to disable or delete system recovery.
Additional Resources
Trellix Labs: RagnarLocker Ransomware Threatens to Release Confidential Information