Old vulnerabilities in new format (unfixable)

There was not much news this week, but all the important ones are in our digest. A couple of updates for the Linux kernel and an old-new vulnerability from Microsoft that has been around for several years. In addition, a little about malware and good news for the victims of REvil.
- Vulnerabilities: unfixable Microsoft bug, couple for Linux and huge Oracle patch;
- Tools: Hash-Buster v3.0, Beaconator, Regexploit and Ppmap;
- News: update malware for macOS developers and REvil key;
- Research: some useful stuff.
Feedback and Vulners docs
Vulnerabilities

SeriousSAM / HiveNightmare
Last week, there was news about a new hype vulnerability in Windows 10 and 11 - CVE-2021-36934 called SeriousSAM or HiveNightmare. And then Benjamin Delpy automated its operation. Benjamin Delpy
Windows has important files with hashed passwords, all OS accounts, encryption key data, and other important information. All this is stored in SAM, SECURITY and SYSTEM:
- C: \ Windows \ System32 \ config \ sam
- C: \ Windows \ System32 \ config \ security
- C: \ Windows \ System32 \ config \ system
The essence of the vulnerability is that if you perform a shadow copy of these files in any way, you can immediately read them with standard user rights. This feature applies to some versions of Windows 10 and 11. In a standard situation, after performing shadow copying, it is impossible to read those specified with user rights.
We recommend that you restrict access to the content of % windir% \ system32 \ config and delete all system restore points and shadow volumes that existed before the access restriction was introduced.
Or, if possible, install the latest Windows updates.

Last week, patches were released for Linux distributions. Both vulnerabilities were discovered by a team of researchers from Qualys and affect the file system.
CVE-2021-33909, titled Sequoia, allows an unprivileged user to gain root privileges on Ubuntu 20.04, Ubuntu 20.10, Ubuntu 21.04, Debian 11, and Fedora 34 Workstation. Other Linux builds are likely to be vulnerable to attacks as well.
CVE-2021-33910 affects the systemd system manager and results in a denial of service. Considering that systemd is used in most Linux distributions, this is a large scale problem. According to the description provided, the exploitation of the vulnerability does not require high rights and it is useless to fight the bug, only installing the appropriate patch will help.
The essence of the vulnerability lies in the incorrect use of the alloca () function, which leads to memory corruption. Thus, an attacker can cause DoS in systemd and the entire OS. To use it, it is enough to mount a file system with a very long path.

Oracle emergency patch
On Tuesday, Oracle released the July 2021 regular update with 342 fixes for several products (Java SE, MySQL, VirtualBox, Solaris, and Weblogic Application Server), some of which could be used by a remote attacker to enslave a vulnerable system.
Chief among them is the re-fix CVE-2019-2729, a critical XMLDecoder deserialization vulnerability in Oracle WebLogic Server web services that can be exploited remotely without authentication. It is worth noting that the vulnerability was initially addressed as part of the June 2019 security update.
Oracle WebLogic Server is an application server that functions as a platform for developing, deploying, and running Java-based enterprise applications.
Six other vulnerabilities have also been patched in WebLogic Server, three of which have a CVSS rating of 9.8 out of 10:
- CVE-2021-2394 (CVSS score: 9.8)
- CVE-2021-2397 (CVSS score: 9.8)
- CVE-2021-2382 (CVSS score: 9.8)
- CVE-2021-2378 (CVSS score: 7.5)
- CVE-2021-2376 (CVSS score: 7.5)
- CVE-2021-2403 (CVSS score: 5.3)
Oracle users are advised to apply the updates as soon as possible to protect the system from potential use.
Tools
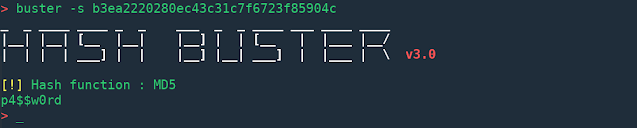
- Automatic hash type identification
- Supports MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512
- Can extract & crack hashes from a file
- Can find hashes from a directory, recursively
- Multi-threading
Beaconator: A beacon generator using Cobalt Strike and PEzor.
Regexploit: Find regexes which are vulnerable to Regular Expression Denial of Service (ReDoS).
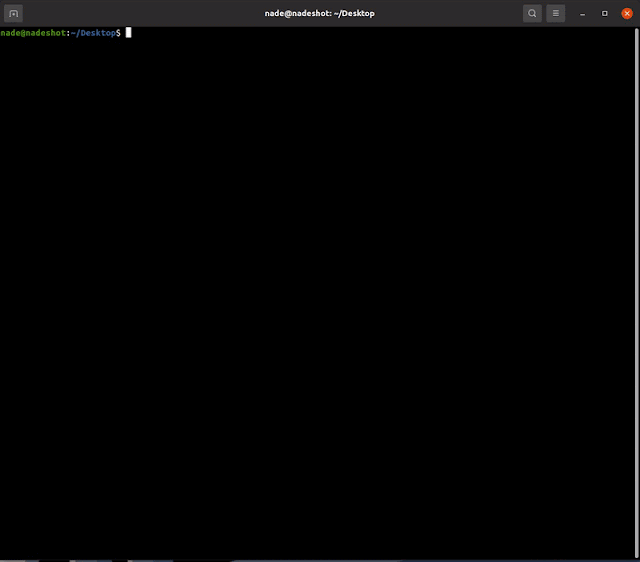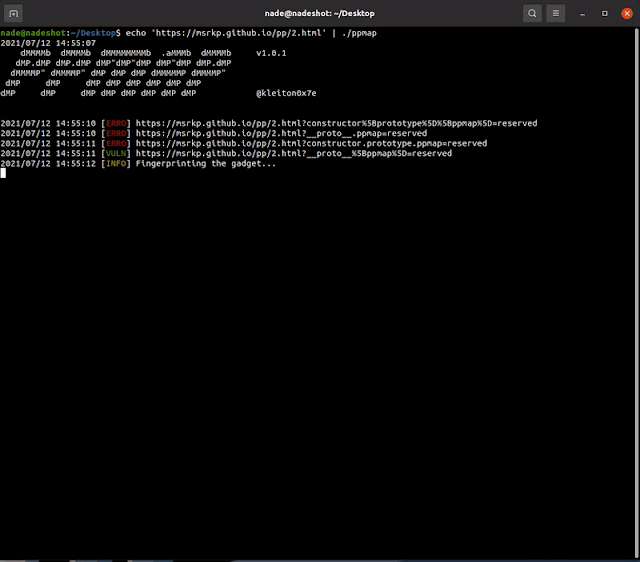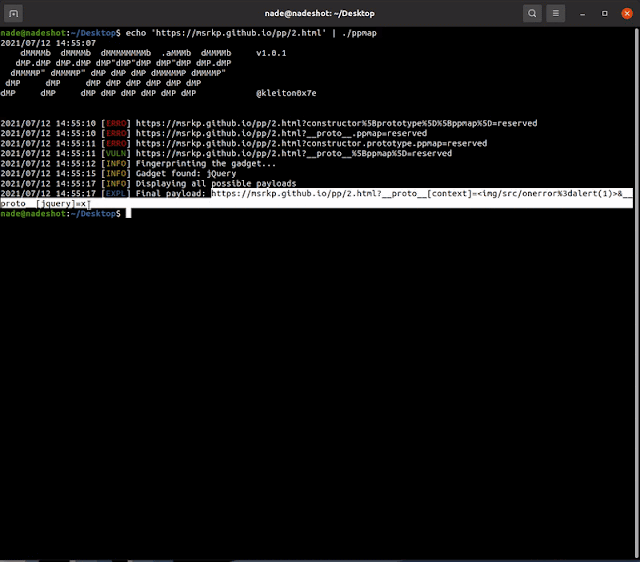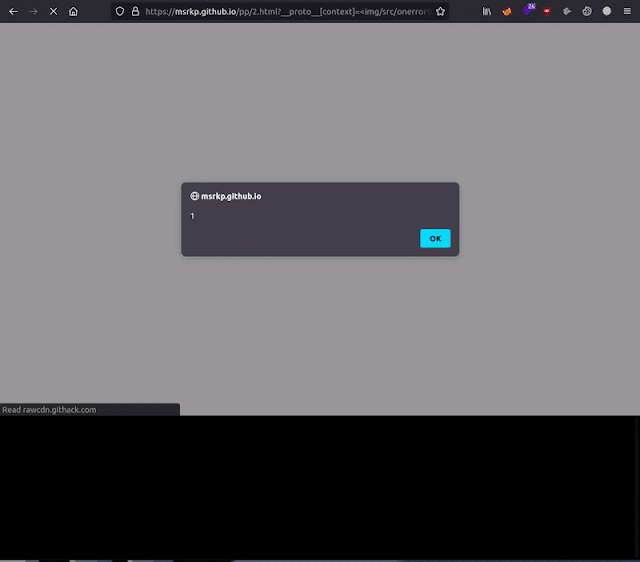
Ppmap: A scanner/exploitation tool, which leverages Prototype Pollution to XSS by exploiting known gadgets
News

XCSSET macOS malware
XCSSET has already been updated this year. The previous update allowed malware authors to attack macOS 11 Big Sur and Macs running on the M1 chipset by bypassing new security policies set by Apple in the latest version of the operating system.
According to a new report released July 22, it was discovered that XCSSET was running a malicious AppleScript file to compress the folder containing the Telegram data ("~ / Library / Group Containers / 6N38VWS5BX.ru.keepcoder.Telegram") into a ZIP file, before uploading it to a remote server under the attacker's control, which allows an attacker to log in using the credentials obtained.
In Google Chrome, the malware attempts to extract passwords stored in a web browser, which in turn are encrypted using a master password, called a "secure storage key," by tricking the user into granting root privileges through a fake dialog box. Next, the command shell is launched to obtain the master key from the iCloud keychain, after which the content is decrypted and transmitted to the server.
The new changes to XCSSET behavior and how malware can extract information from popular attachments demonstrates how aggressively authors are willing to act to retrieve sensitive data from affected systems.

REvil key
Almost three weeks later, after failed negotiations and unsuccessful attempts to obtain the decryption key, Kaseya finally got hold of the universal decryptor of the REvil ransomware to unlock the systems and help the affected customers recover their data.
The legitimacy and effectiveness of the newly obtained Kaseya key was confirmed even by Emsisoft, which was hired by the developer to help clients recover and eliminate the consequences of the incident.
Research
The Evolution of a Matrix: How ATT&CK for Containers was Built
Windows Command-Line Obfuscation
https://m.youtube.com/watch?v=PiYPLEjYXnw
Implementing RITA using KQL: https://posts.bluraven.io/implementing-rita-using-kql-8ccb0ee8eeae
The Evolution of a Matrix: How ATT&CK for Containers was Built
Cyber Defense Follow the Indicators of Compromise (IOC) Breadcrumbs
Feedback
x-how-attck-for-containers-was-built/)
Cyber Defense Follow the Indicators of Compromise (IOC) Breadcrumbs
