Details Released for Recently Patched new macOS Archive Utility Vulnerability
5.5 Medium
CVSS3
Attack Vector
LOCAL
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
NONE
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
NONE
CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:N
4.3 Medium
CVSS2
Access Vector
NETWORK
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
NONE
Integrity Impact
PARTIAL
Availability Impact
NONE
AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:N/I:P/A:N
Security researchers have shared details about a now-addressed security flaw in Apple’s macOS operating system that could be potentially exploited to run malicious applications in a manner that can bypass Apple’s security measures.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-32910, is rooted in the built-in Archive Utility and “could lead to the execution of an unsigned and unnotarized application without displaying security prompts to the user, by using a specially crafted archive,” Apple device management firm Jamf said in an analysis.
Following responsible disclosure on May 31, 2022, Apple addressed the issue as part of macOS Big Sur 11.6.8 and Monterey 12.5 released on July 20, 2022. The tech giant, for its part, also revised the earlier-issued advisories as of October 4 to add an entry for the flaw.
Apple described the bug as a logic issue that could allow an archive file to get around Gatekeeper checks, which is designed so as to ascertain that only trusted software runs on the operating system.
The security technology achieves this by verifying that the downloaded package is from a legitimate developer and has been notarized by Apple – i.e., given a stamp of approval to ensure it’s not been maliciously tampered with.
“Gatekeeper also requests user approval before opening downloaded software for the first time to make sure the user hasn’t been tricked into running executable code they believed to simply be a data file,” Apple notes in its support documentation.
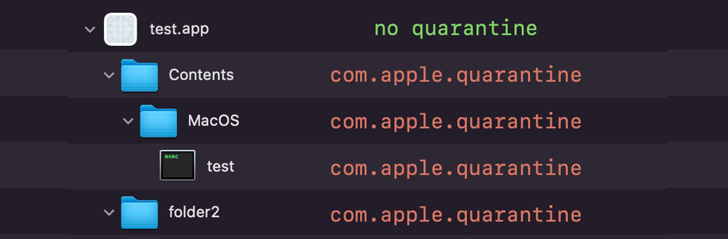
It’s also worth noting archive files downloaded from the internet are tagged with the “com.apple.quarantine” extended attribute, including the items within the file, so as to trigger a Gatekeeper check prior to execution.
But in a peculiar quirk discovered by Jamf, it was found that the Archive Utility fails to add the quarantine attribute to a folder “when extracting an archive containing two or more files or folders in its root directory.”
Thus by creating an archive file with the extension “exploit.app.zip,” it leads to a scenario where an unarchival results in the creation of a folder titled “exploit.app,” while also lacking the quarantine attribute.
This application “will bypass all Gatekeeper checks allowing an unnotarized and/or unsigned binary to execute,” Jamf researcher Ferdous Saljooki, who discovered the flaw, said. Apple said it resolved the vulnerability with improved checks.
The findings come more than six months after Apple addressed another similar flaw in macOS Catalina, Big Sur 11.6.5, and Monterey 12.3 (CVE-2022-22616) that could allow a malicious ZIP archive to bypass Gatekeeper checks.
Found this article interesting? Follow THN on Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.
5.5 Medium
CVSS3
Attack Vector
LOCAL
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
NONE
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
NONE
CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:H/A:N
4.3 Medium
CVSS2
Access Vector
NETWORK
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
NONE
Integrity Impact
PARTIAL
Availability Impact
NONE
AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:N/I:P/A:N