CVE Vulnerability Score: Definition & Analysis

- CVE and CVSS
- What is CVE?
- How does the CVE system work?
- What is CVSS?
- How effective is Vulners vulnerability database
- Conclusion
- FAQ
CVE and CVSS
CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is the cyber industry's basic template for reporting common security vulnerabilities. This classification system was created in 1999 by the government-funded research company MITRE to meet the pressing demand in the cyber-sec community for a solution to define and sort the known and new weak spots in their information security environments.
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) is the industry go-to standard for calculating the severity of any given vulnerability.
What is CVE?
CVE serves as more than just a database. It equips users with the knowledge to maintain efficient basic vulnerability management across their infrastructure. By understanding the weaknesses of the infrastructure, cybersecurity experts can better assess their risks, and apply the knowledge base more effectively to reach peak performance of their security tools.
Vulners is known for being the most complete and correlated vulnerability database on the market. Visit vulners.com/ for more information and top-tier vulnerability management.
How does the CVE system work?
The main purpose of CVE is to standardize the methods of identifying and describing vulnerabilities or security threats. This includes a unique identifier, a description of the vulnerability, and at least one publicly available reference. CVE is a publicly available and royalty-free threat classifier. Let us examine the identifier code CVE-2020-16891 and see what it tells us. The ID contains the CVE prefix, the year the vulnerability was discovered, and its numeric sequence number.
The CVE details contain the name of the affected product, its manufacturer, a summary of affected versions, vulnerability type, exploitation impact, access level for attackers to exploit the vulnerability, and critical code components or inputs involved.
What is CVSS?
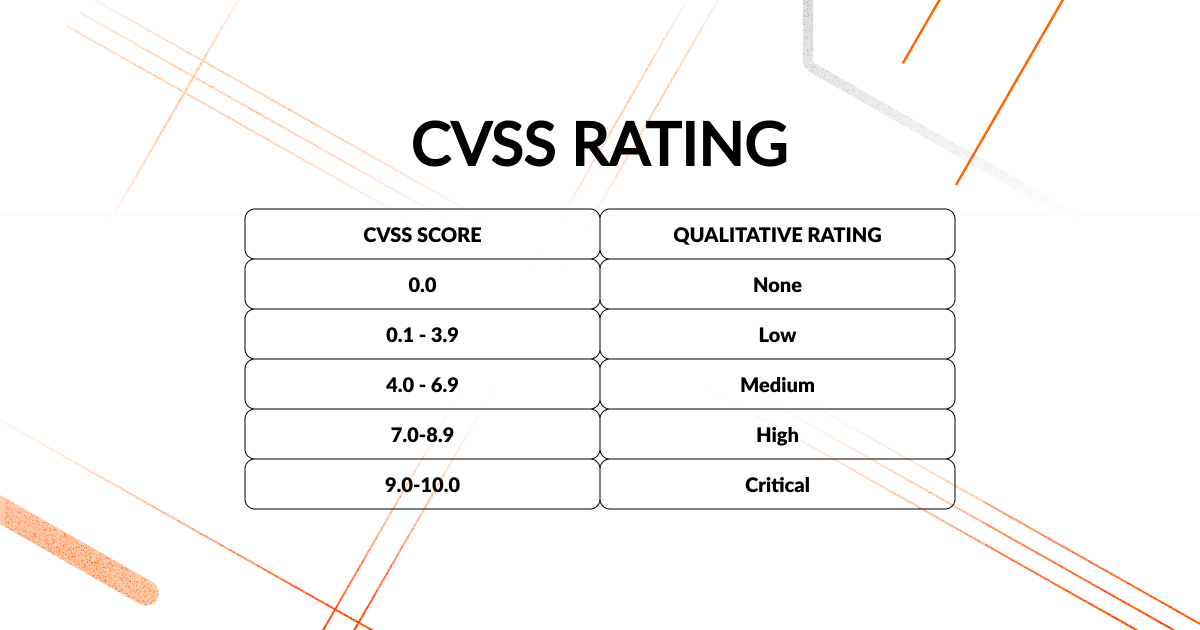
We have already defined CVSS as being a free and open industry standard for assessing the severity of computer vulnerabilities. CVSS is used to assign degrees of severity to vulnerabilities expressed by a base score from 0.0 to 10.0, where 10.0 is the most severe.
The table below shows the CVSS correlation between the numeric score and the severity expression.
The scoring process involves factoring in the three metrics as follows:
- Base metric. Qualitative vulnerability assessment, which does not depend on time or software environment
- Temporal metrics. Such metrics take into account the response of the manufacturer of the vulnerable product, which change from the moment the vulnerability is discovered until it is patched.
- Environmental metrics. Vulnerability metrics that take into account the specific security requirements of the system that hosts the vulnerable product
These 3 categories are further subdivided into smaller metrics like the Access Vector (AV), which shows how a vulnerability can be exploited, or something like Collateral Damage Potential (CDP), which measures the degree of unintended aftermath following an exploit. Later versions of CVSS added more precision and sophistication to the assessment. More variables and longer formulas indeed render more accurate scores, though at the expense of practicality. There are plenty of articles out there to criticize this scoring system, but today, we will grant it the respect it deserves. Largely for the fact that it was a much-needed solution back in the day, so its creation was a huge milestone for communication within the security community.
CVE analysis
Since CVEs are real documented records of known security flaws, having access to a database of such information and the ability to apply it correctly can greatly improve any company’s security posture. Although, the mere existence of CVEs does not protect your perimeter, they can be used as input data to test your perimeter against what definitely know is out there.
CVE-less vulnerabilities
Given the annual rate at which new vulnerabilities are submitted to the record (approximately 25,000 for year 2022), it might seem like CVE is a “welcome all” club. However, not all bugs are assigned a CVE. These are vulnerabilities with no identifier, no CVSS, no explicit labeling, or it may be that such vulnerabilities have not been acknowledged by their vendor. As a result, such vulnerabilities may have no common description, rating, or available patches. This makes them difficult to work with, assess, and prevent their exploitation, but finding a solution for this could very well be the next milestone in the cybersecurity industry. But for now, all we can do is actively source relevant information from bug-bounty and zero-day reports.
How effective is Vulners vulnerability database
Vulners keeps finding new feeds and coming up with new ways to enrich and correlate its database. The team’s success is reflected in the company’s reputation as being the world's most up-to-date vulnerability database. And what they deliver to their users is confidence and reliability. With Vulners you could easily gain an edge in vulnerability management. The website vulners.com/ is free to register and explore. The website provides its users with invaluable support in the form of 250k+ exploits for popular vulnerabilities as well as 2mln+ advisories and articles.
Conclusion
No matter your attitude towards the CVE and the CVSS, it is still beyond any doubt that these systems of reporting and prioritizing vulnerabilities are an important step in the evolution of cybersecurity. The standardized nature of these systems allows for more flexibility to use them in both simple and complex infrastructures.
FAQ
Do all vulnerabilities have a CVE?
This is not the case. Keep in mind that out of the 25,000 vulnerabilities discovered in 2023, about 40% of them have been left without a CVE number. In other words, all CVEs are vulnerabilities, but not all vulnerabilities have CVEs
What is the impact of the CVE vulnerability?
The beauty of CVE is that the vulnerabilities it describes have been reviewed and approved, so their effects can be anticipated and mitigated. And even more importantly, this information can be used as input data for assessing the weaknesses of your IT infrastructure.
