Vulners NASL Plugin Feeds for OpenVAS 9
7 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
LOCAL
Attack Complexity
HIGH
Privileges Required
LOW
User Interaction
NONE
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:H/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
6.9 Medium
CVSS2
Access Vector
LOCAL
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
COMPLETE
Integrity Impact
COMPLETE
Availability Impact
COMPLETE
AV:L/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C
0.001 Low
EPSS
Percentile
24.8%
As I already wrote earlier, you can easily add third party nasl plugins to OpenVAS. So, my friends from Vulners.com realised generation of NASL plugins for OpenVAS using own security content. I’ve tested it for scanning CentOS 7 host. And it works =)
Let’s see the whole process.
I assume that we have installed OpenVAS 9 from sources using openvas-commander script.
I am going to the OpenVAS server and run all commands as root:
ssh [email protected] su
Cleaning NVT cache and updating plugins from Greenbone feed
If you already were experimenting with own NASL scripts, it’s may be a good clear the OpenVAS vulnerability base.
Deleting cache and plugins for 2017:
find /usr/local/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2017/ | grep "nasl" | xargs -i rm '{}' find /usr/local/var/cache/openvas/2017/ | grep ".nvti" | xargs -i rm '{}'
Updating Greenbone content:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/leonov-av/openvas-commander/master/openvas_commander.sh chmod +x openvas_commander.sh ./openvas_commander.sh --update-content-nvt ./openvas_commander.sh --kill-all ./openvas_commander.sh --start-all ps -aux | grep "openvassd" # Wait untill openvassd 100% reloaded
Rebuilding cache:
openvasmd --rebuild --progress
Output:
Rebuilding NVT cache... |
done.
And restart once again:
./openvas_commander.sh --kill-all ./openvas_commander.sh --start-all ps -aux | grep "openvassd" # Wait untill openvassd 100% reloaded
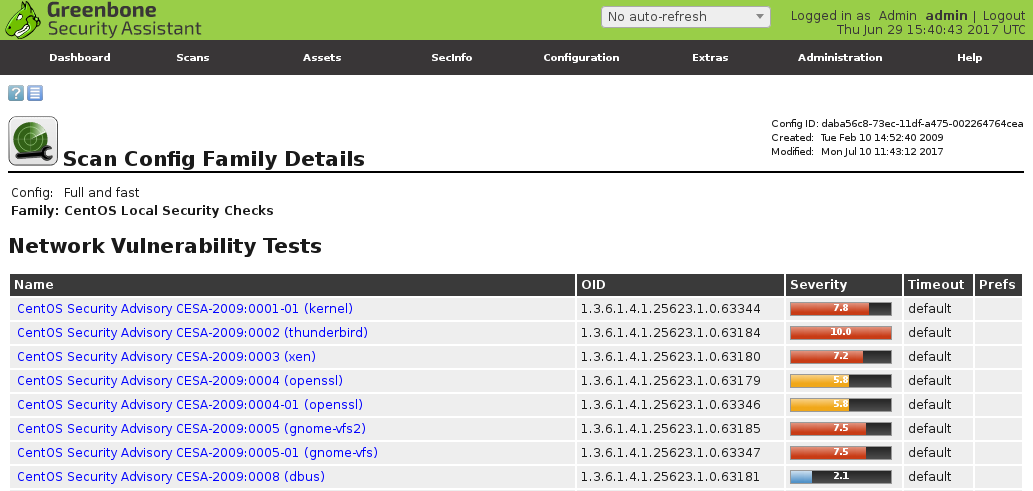
Checking that there is no third-party plugins in GSM:
Seems good.
Adding Vulners NASL scripts
You can get a link to an archive at <https://vulners.com/stats> (icon with gear)

curl -k https://vulners.com/api/v3/archive/nasl/?type=centos > vulners_nasl.zip unzip vulners_nasl.zip -d vulners_nasl cp vulners_nasl/* /usr/local/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2017/
Restart OpenVAS:
./openvas_commander.sh --kill-all ./openvas_commander.sh --start-all ps -aux | grep "openvassd" # Wait untill openvassd 100% reloaded
And rebuild NVT cache:
openvasmd --rebuild --progress
Output:
Rebuilding NVT cache... |
done.
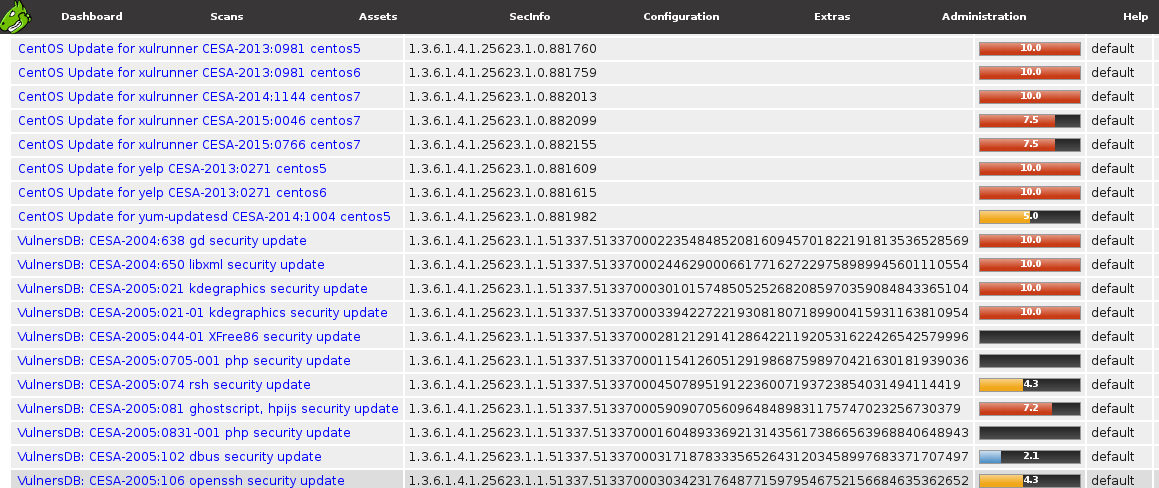
Checking Vulners plugins in GSM:
Both Greenbone and Vulners.com plugins here. Great!
Scanning CentOS host
I created a simple authenticated scanning task and launched it:
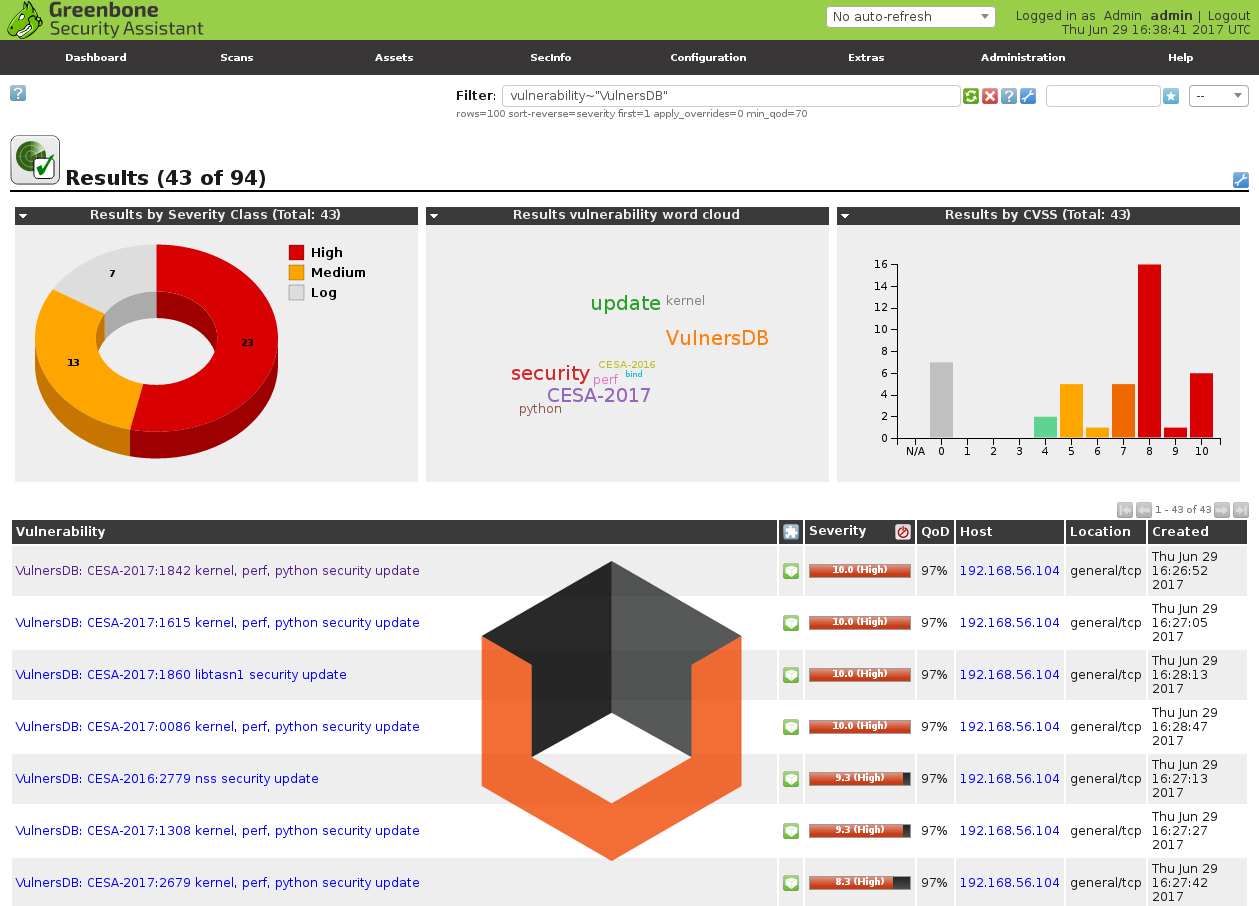
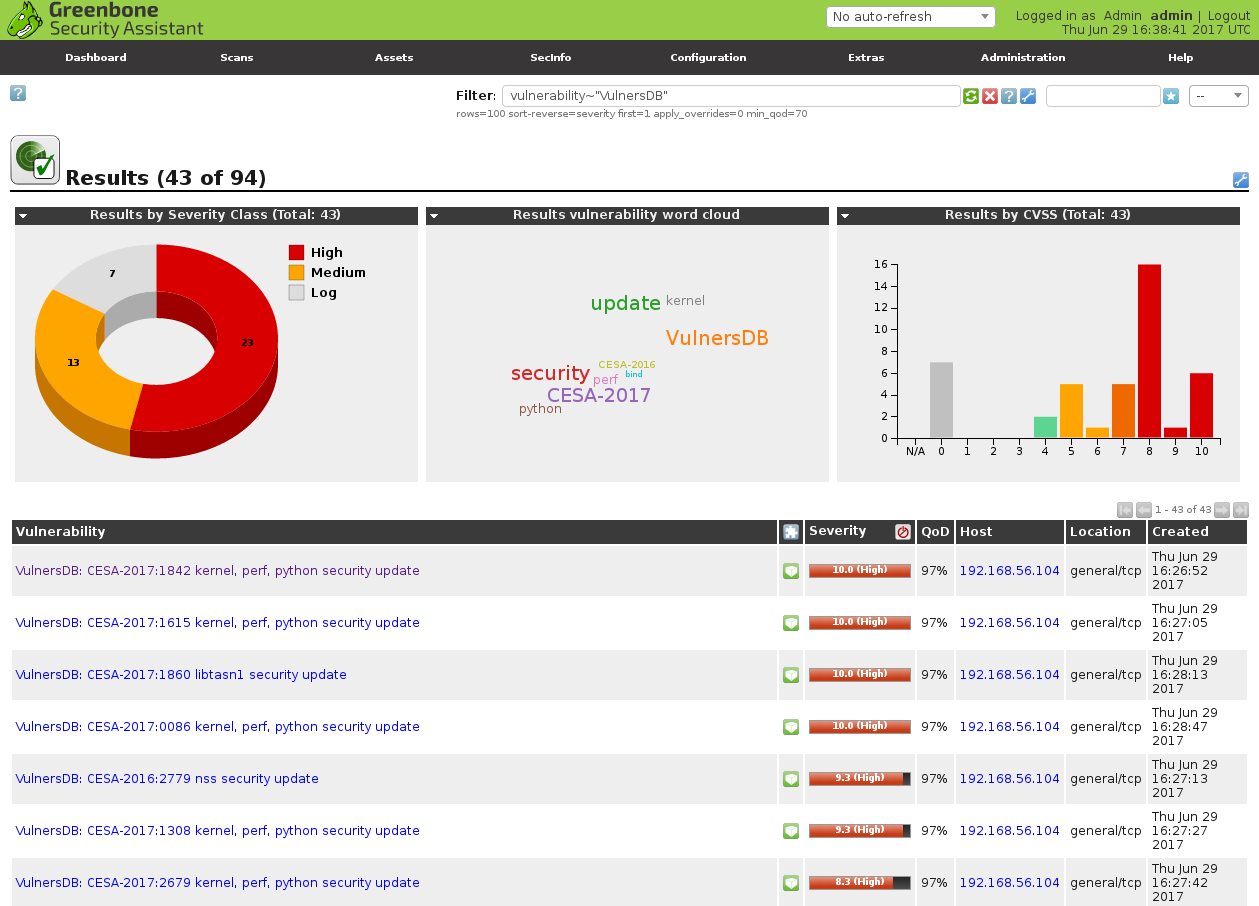
Some minutes letter I have the results, that I can easily filter. For example, show vulnerabilities detected by Vulners nasl plugins:
vulnerability~"VulnersDB"
Plugin data:
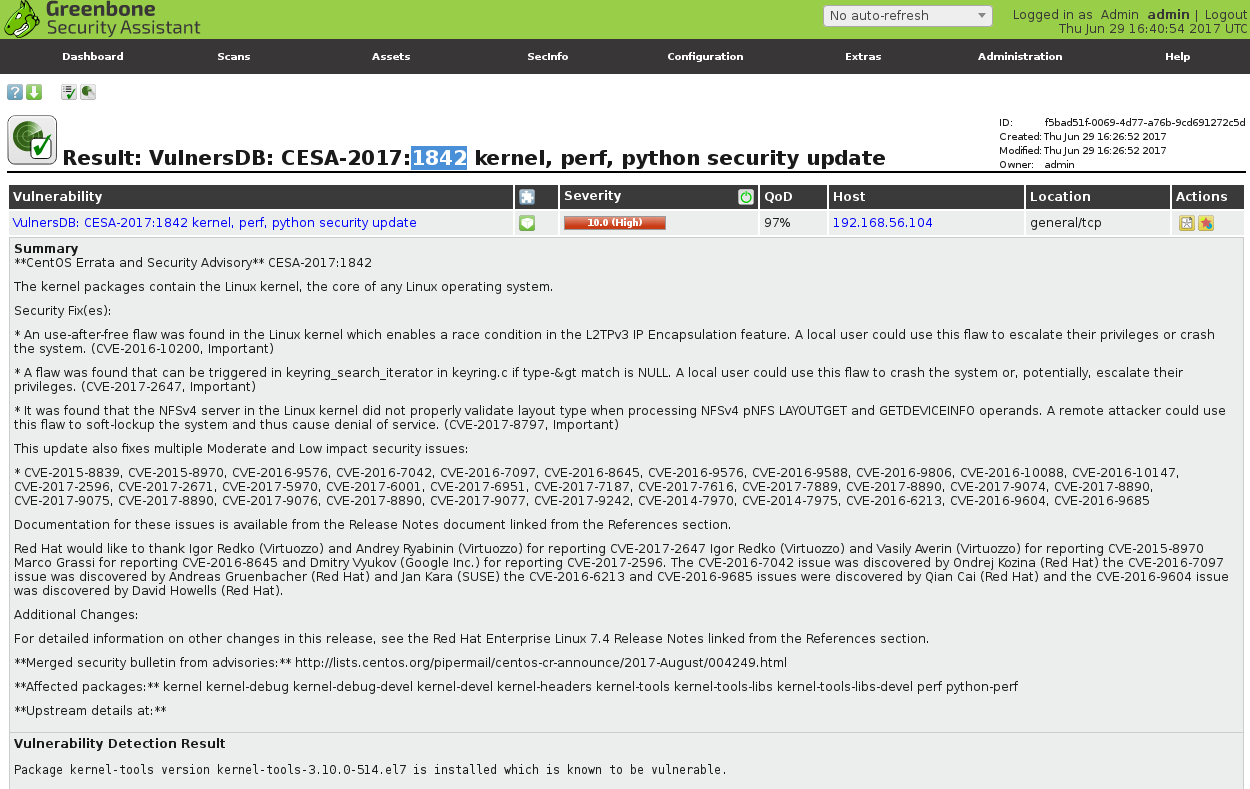
Plugin text on Vulners.com website: <https://vulners.com/api/v3/nasl/id/?id=CESA-2017:1842>
###############################################################################
# OpenVAS centos Vulnerability Test
#
# kernel, perf, python security update
#
# Authors:
# Kir Ermakov
# Igor Bulatenko
# Ivan Elkin
# Alex Leonov
#
# Copyright:
# Copyright (C) 2017 Vulners.com, https://vulners.com
#
# This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
...
# Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
###############################################################################
if(description)
{
script_oid("1.3.6.1.4.1.25623.1.1.51337.5133700027808229620542704492639841805966348423");
script_version("$Revision: 1 $");
script_tag(name:"last_modification", value:"$Date: 2017-08-24T01:38:33 $");
script_tag(name:"creation_date", value:"$Date: 2017-08-24T01:38:33 $");
script_cve_id("CVE-2016-9604",...,"CVE-2014-7970");
script_tag(name:"cvss_base", value:"10.0");
script_tag(name:"cvss_base_vector", value:"AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C");
script_tag(name:"qod_type", value:"package");
script_name("VulnersDB: CESA-2017:1842 kernel, perf, python security update");
script_tag(name: "summary", value: "**CentOS Errata and Security Advisory** CESA-2017:1842
The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system.
Security Fix(es):
* An use-after-free flaw was found in the Linux kernel which enables a race condition in the L2TPv3 IP Encapsulation feature. A local user could use this flaw to escalate their privileges or crash the system. (CVE-2016-10200, Important)
...
**Affected packages:**
kernel
...
python-perf
**Upstream details at:**
");
script_tag(name: "vuldetect", value: "Get the installed version with the help of detect NVT and check if the version is vulnerable or not.");
script_tag(name: "affected", value: "
kernel-tools on CentOS 7 ,
...
kernel-debug-devel on CentOS 7 ,
kernel-headers on CentOS 7 ,
perf on CentOS 7 ,");
script_tag(name: "solution", value: "Please Install the Updated Packages.");
script_tag(name:"solution_type", value:"VendorFix");
script_xref(name: "URL" , value: "http://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-cr-announce/2017-August/004249.html");
script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO);
script_copyright("Copyright (C) 2017 Vulners");
script_xref(name: "CESA", value: "CESA-2017:1842");
script_family("CentOS Local Security Checks");
script_dependencies("gather-package-list.nasl");
script_mandatory_keys("HostDetails/OS/cpe:/o:centos:centos", "login/SSH/success", "ssh/login/release");
exit(0);
}
include("revisions-lib.inc");
include("pkg-lib-rpm.inc");
release = get_kb_item("ssh/login/release");
res = "";
if(release == NULL){
exit(0);
}
if(release == "CentOS7")
{
if ((res = isrpmvuln(pkg:"kernel-tools", rpm:"kernel-tools~3.10.0~693.el7", rls:"CentOS7")) != NULL)
{
security_message(data:res);
exit(0);
}
}
...
if (__pkg_match) exit(99); # Not vulnerable.
exit(0);
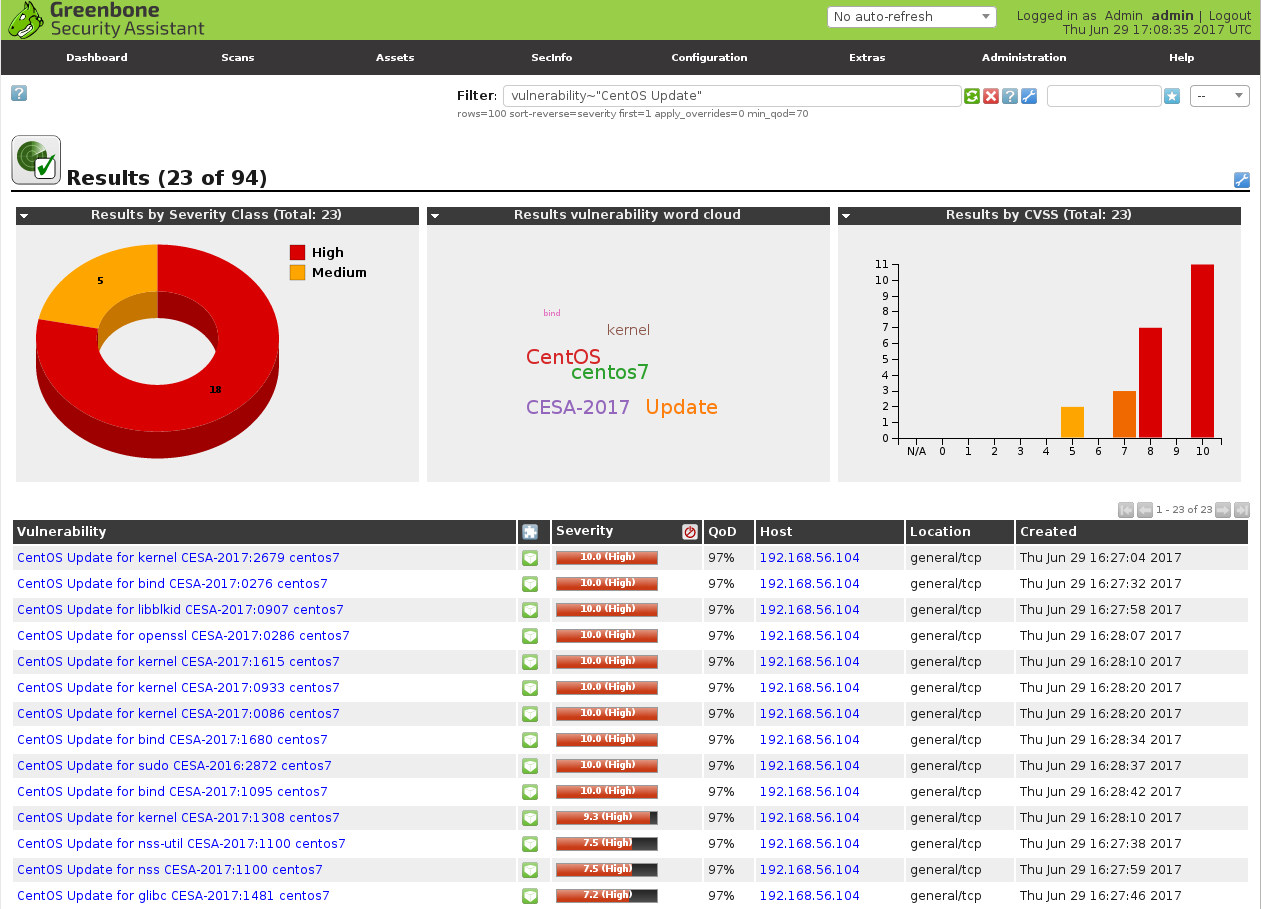
I can also filter vulnerabilities detected only by Greenbone plugins.
vulnerability~"CentOS Update"
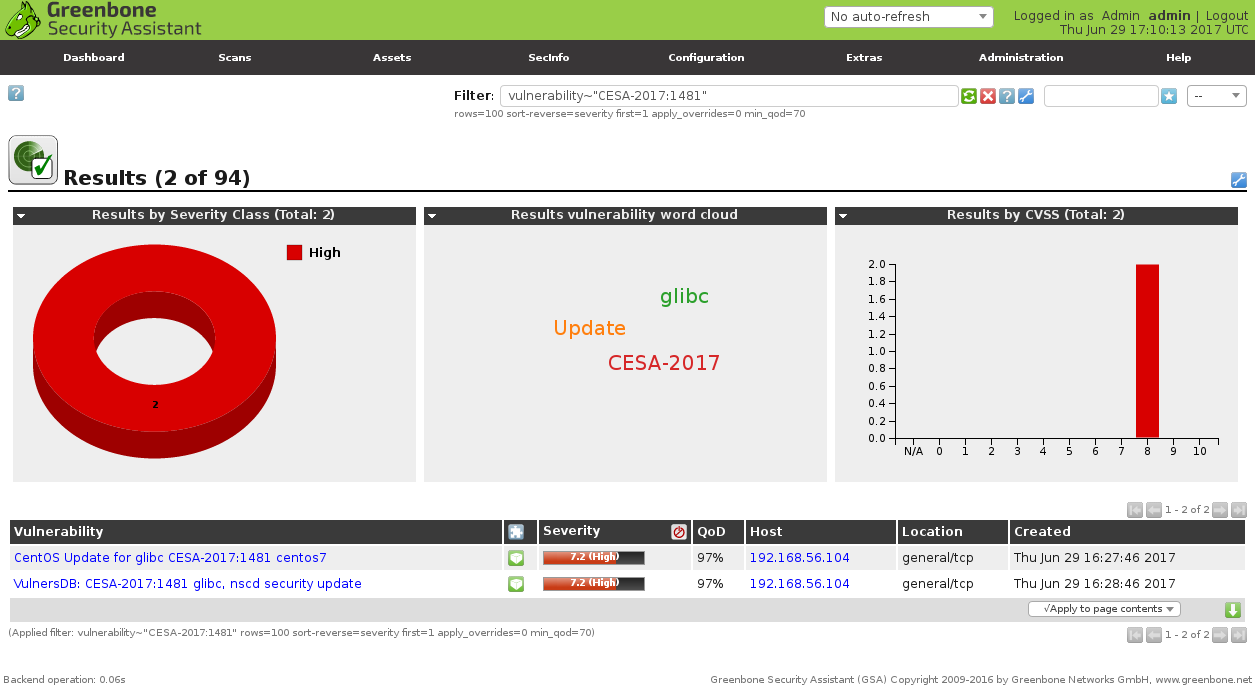
As you can see on dashboards the results are not fully the same. Some vulnerabilities both Greenbone and Vulners found.
vulnerability~"CESA-2017:1481"
But, for example, CESA-2017:1842 that I have shown above on a sreenshot was detected only by Vulners plugins.
The plugin says that kernel-tools-3.10.0-514.el7 is vulnerable.
And it is, according to bulletin <https://vulners.com/centos/CESA-2017:1842>:
CentOS 7 x86_64 kernel-tools < 3.10.0-693.el7 kernel-tools-3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64.rpm
The answer is that Greenbone feed doesn’t contain this plugin (yet):
# ls /usr/local/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2017/gb_CESA-2017_1842* ls: cannot access /usr/local/var/lib/openvas/plugins/2017/gb_CESA-2017_1842*: No such file or directory
7 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
LOCAL
Attack Complexity
HIGH
Privileges Required
LOW
User Interaction
NONE
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:H/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
6.9 Medium
CVSS2
Access Vector
LOCAL
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
COMPLETE
Integrity Impact
COMPLETE
Availability Impact
COMPLETE
AV:L/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C
0.001 Low
EPSS
Percentile
24.8%