
Microsoft Patch Tuesday September 2020: Zerologon and other exploits, RCEs in SharePoint and Exchange
8.8 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
NETWORK
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
9.3 High
CVSS2
Access Vector
NETWORK
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
COMPLETE
Integrity Impact
COMPLETE
Availability Impact
COMPLETE
AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C
I would like to start this post by talking about Microsoft vulnerabilities, which recently turned out to be much more serious than it seemed at first glance.
Older Vulnerabilities with exploits
"Zerologon" Netlogon RCE (CVE-2020-1472)
One of them is, of course, the Netlogon vulnerability from the August 2020 Patch Tuesday. It's called "Zerologon". I would not say that Vulnerability Management vendors completely ignored it. But none of them (well, maybe only ZDI) emphasized in their reports that this vulnerability would be a real disaster.

Why? Because there were no details and there were no public exploits back then. That started to change dramatically when the full review by Secura was published.
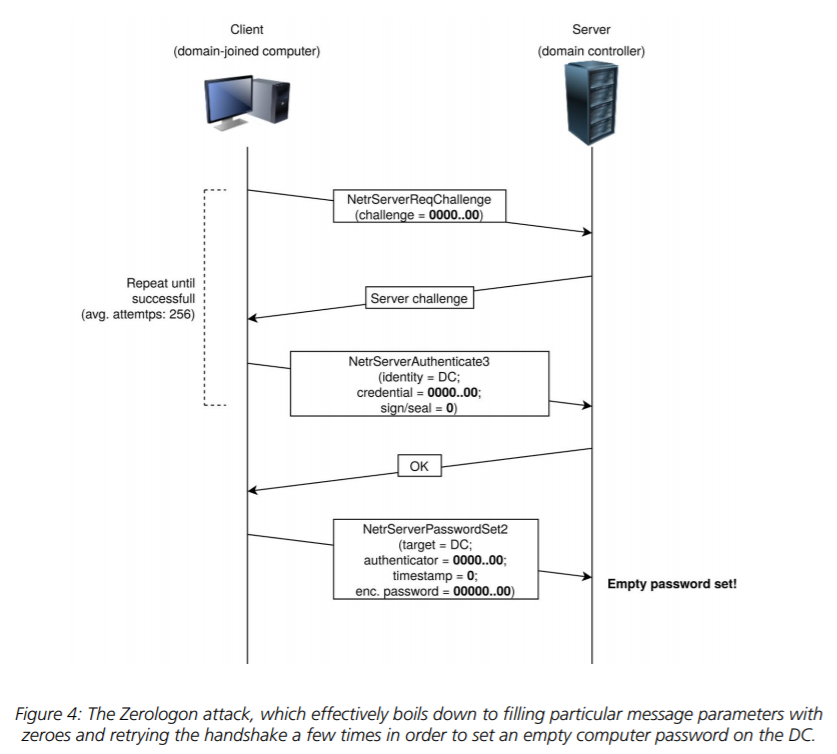
It became clear that this was not a privilege escalation. In fact, it was Remote Code Execution without authentication. Then an exploit appeared on Github. It was tested and approved by experts.
> We have reproduced the CVE-2020-1472 #zerologon vulnerability! It's an unauth RCE for Domain Controllers. pic.twitter.com/qFe45O7WPR
>
> – PT SWARM (@ptswarm) September 14, 2020
After this all the Vulnerability Management vendors (Qualys, Tenable, Rapid7) made their blog posts about this vulnerability. And CISA even released an Emergency Directive to patch all the Domain Controllers of Federal Agencies in just 4 days!

An exploit for this vulnerability has become available in Mimikatz.
> A new #mimikatz  release with #zerologon / CVE-2020-1472 detection, exploit, DCSync support and a lots of love inside
release with #zerologon / CVE-2020-1472 detection, exploit, DCSync support and a lots of love inside 
It now uses direct RPC call (fast and supports unauthenticated on Windows)
> <https://t.co/Wzb5GAfWfd>
Thank you: @SecuraBV pic.twitter.com/s7LRRLPRTP
>
> –  Benjamin Delpy (@gentilkiwi) September 16, 2020
Benjamin Delpy (@gentilkiwi) September 16, 2020
And so it was not surprising when Microsoft began to detect the real life exploitations all this vulnerability.
> Microsoft is actively tracking threat actor activity using exploits for the CVE-2020-1472 Netlogon EoP vulnerability, dubbed Zerologon. We have observed attacks where public exploits have been incorporated into attacker playbooks.
>
> — Microsoft Security Intelligence (@MsftSecIntel) September 24, 2020
And the story is far from over. For example there is an article about new methods of exploiting this vulnerability that doesn't require the change of the password, so it will be harder to detect such exploitation.
EoPs in Microsoft Spooler (CVE-2020-1048) and Windows Update Orchestrator (CVE-2020-1313)
Some more examples without so much hype. It's about an appearance of public exploits for
- Microsoft Spooler Elevation of Privilege (CVE 2020-1048, MSF:EXPLOIT/WINDOWS/LOCAL/CVE_2020_1048_PRINTERDEMON) from Microsoft Patch Tuesday May 2020
- Microsoft Windows Update Orchestrator Elevation of Privilege (CVE-2020-1313, PACKETSTORM:159305) from Microsoft Patch Tuesday June 2020
This is interesting because all the Vulnerability Management vendors simply ignored these vulnerabilities in their Patch Tuesday reviews.  Who could say that these two would be really exploitable among hundreds others?
Who could say that these two would be really exploitable among hundreds others?
Vulnerability prioritization is not a silver bullet
I think it's just a good demonstration that vulnerability prioritization is not a silver bullet and if you want to protect your infrastructure, you should install all the patches on all the hosts or monitor security news carefully (and doing both is even better). For monitoring I use my own telegram channel @avleonovnews. It updates automatically, and the script not only shows news from different feeds, but also tries to highlight everything related to vulnerabilities, exploits, patches, etc. So, I invite you to check it out.
September 2020 Patch Tuesday
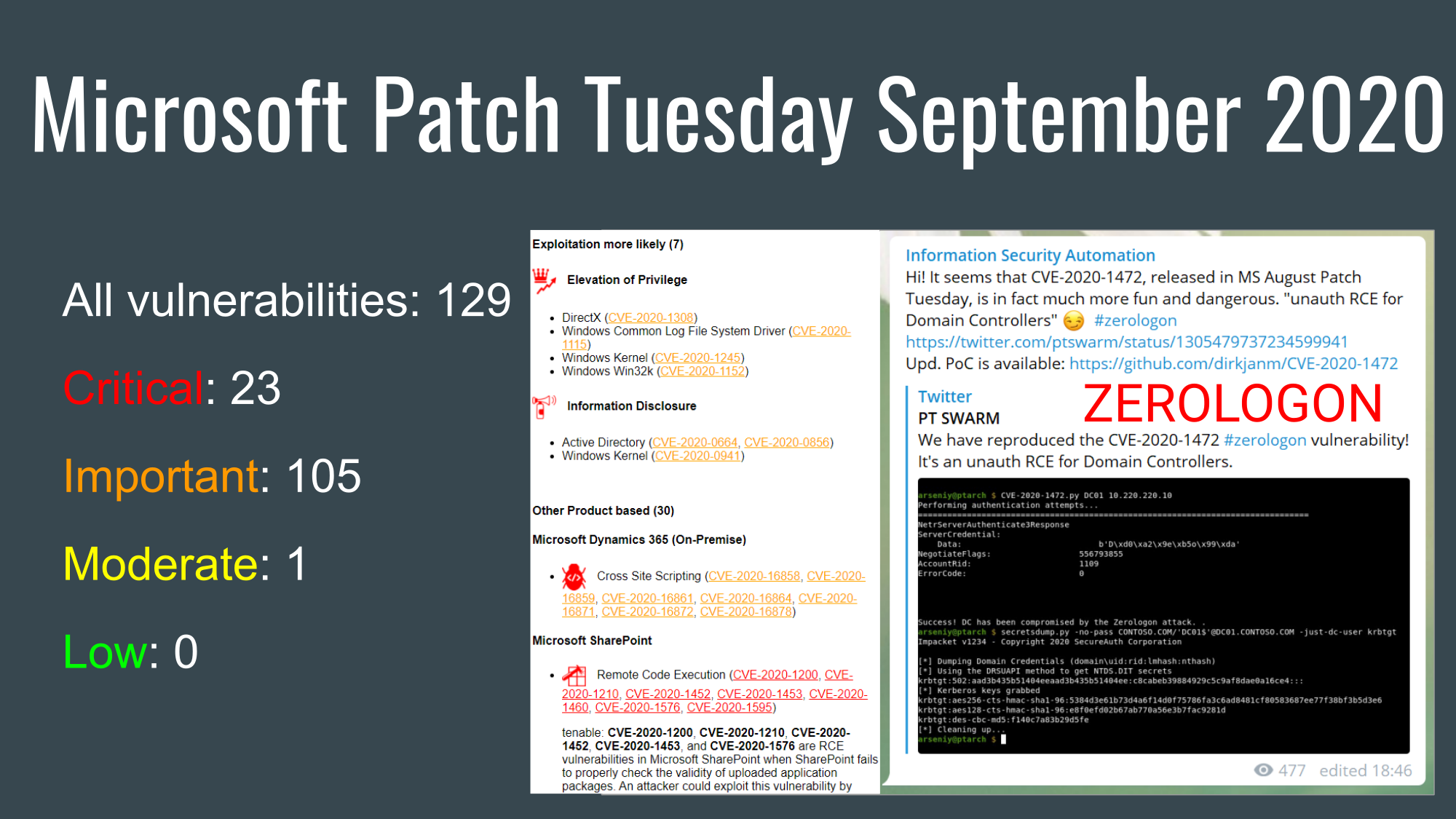
Now let's finally look at the September vulnerabilities. There were 129 vulnerabilities: 23 of them were critical, 105 were important and 1 was moderate. There were no vulnerabilities with detected exploitation.
Exploitation more likely (7)
There were 7 vulnerabilities marked as "Exploitation more likely". But none of them were mentioned by Vulnerability Management vendors. Probably it's because there were no RCEs, only Elevation of Privilege and Information Disclosure.
 Elevation of Privilege
Elevation of Privilege
- DirectX (CVE-2020-1308)
- Windows Common Log File System Driver (CVE-2020-1115)
- Windows Kernel (CVE-2020-1245)
- Windows Win32k (CVE-2020-1152)
 Information Disclosure
Information Disclosure
- Active Directory (CVE-2020-0664, CVE-2020-0856)
- Windows Kernel (CVE-2020-0941)
Other Product based (30)
The software products with the most vulnerabilities were Microsoft Dynamics 365 (On-Premise), Microsoft SharePoint and Windows Kernel. Vulnerability Management vendors focussed on Microsoft SharePoint Remote Code Execution vulnerabilities. There were 7 of them (CVE-2020-1200, CVE-2020-1210, CVE-2020-1452, CVE-2020-1453, CVE-2020-1460, CVE-2020-1576, CVE-2020-1595)! Only one, CVE-2020-1460, requires authentication. Rapid7 also mentions two rare "Tampering" SharePoint vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-1440, CVE-2020-1523). "Fortunately, the description on this vulnerability does say prior authentication on an affected SharePoint Server is required, but with that in hand, an attacker can target specific users and alter the targets profile data."
Microsoft Dynamics 365 (On-Premise)
 Cross Site Scripting (CVE-2020-16858, CVE-2020-16859, CVE-2020-16861, CVE-2020-16864, CVE-2020-16871, CVE-2020-16872, CVE-2020-16878)
Cross Site Scripting (CVE-2020-16858, CVE-2020-16859, CVE-2020-16861, CVE-2020-16864, CVE-2020-16871, CVE-2020-16872, CVE-2020-16878)
Microsoft SharePoint
 Remote Code Execution (CVE-2020-1200, CVE-2020-1210, CVE-2020-1452, CVE-2020-1453, CVE-2020-1460, CVE-2020-1576, CVE-2020-1595)
Remote Code Execution (CVE-2020-1200, CVE-2020-1210, CVE-2020-1452, CVE-2020-1453, CVE-2020-1460, CVE-2020-1576, CVE-2020-1595) Cross Site Scripting (CVE-2020-1198, CVE-2020-1227, CVE-2020-1345, CVE-2020-1482, CVE-2020-1514, CVE-2020-1575)
Cross Site Scripting (CVE-2020-1198, CVE-2020-1227, CVE-2020-1345, CVE-2020-1482, CVE-2020-1514, CVE-2020-1575) Spoofing (CVE-2020-1205)
Spoofing (CVE-2020-1205) Tampering (CVE-2020-1440, CVE-2020-1523)
Tampering (CVE-2020-1440, CVE-2020-1523)
Windows Kernel
 Elevation of Privilege (CVE-2020-1034)
Elevation of Privilege (CVE-2020-1034) Information Disclosure (CVE-2020-0928, CVE-2020-1033, CVE-2020-1250, CVE-2020-1589, CVE-2020-1592, CVE-2020-16854)
Information Disclosure (CVE-2020-0928, CVE-2020-1033, CVE-2020-1250, CVE-2020-1589, CVE-2020-1592, CVE-2020-16854)
Other Vulnerability Type based (92)
Among other vulnerabilities, the most interesting, of course, are various Remote Code Executions.
A funny story happened with RCE in Microsoft Exchange Server (CVE-2020-16875). All Vulnerability Management vendors marked it as top priority. But Microsoft later changed the description to indicate the bug can only be reached by an authenticated user. So, the risk became much lower.
Other RCE groups mentioned by Vulnerability Management vendors:
- Browser-related RCEs in Chakra Scripting Engine (CVE-2020-1180, CVE-2020-1057, CVE-2020-1172), Microsoft Browser (CVE-2020-0878)
- Office-related RCEs in Microsoft Excel (CVE-2020-1193, CVE-2020-1332, CVE-2020-1335, CVE-2020-1594), Microsoft Word (CVE-2020-1218, CVE-2020-1338)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises) (CVE-2020-16860, CVE-2020-16862, CVE-2020-16857)
- Windows systems components: Microsoft COM for Windows (CVE-2020-0922), Microsoft Windows Codecs Library (CVE-2020-1129, CVE-2020-1319), and simply Windows (CVE-2020-1252)
 Remote Code Execution
Remote Code Execution
- Active Directory (CVE-2020-0718, CVE-2020-0761)
- Chakra Scripting Engine (CVE-2020-1180, CVE-2020-1057, CVE-2020-1172)
- GDI+ (CVE-2020-1285)
- Internet Explorer Browser Helper Object (BHO) (CVE-2020-16884)
- Jet Database Engine (CVE-2020-1039, CVE-2020-1074)
- Microsoft Browser (CVE-2020-0878)
- Microsoft COM for Windows (CVE-2020-0922)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises) (CVE-2020-16860, CVE-2020-16862)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Finance and Operations (on-premises) (CVE-2020-16857)
- Microsoft Excel (CVE-2020-1193, CVE-2020-1332, CVE-2020-1335, CVE-2020-1594)
- Microsoft Exchange Server (CVE-2020-16875)
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library (CVE-2020-1129, CVE-2020-1319)
- Microsoft Word (CVE-2020-1218, CVE-2020-1338)
- Visual Studio (CVE-2020-16856, CVE-2020-16874)
- Visual Studio JSON (CVE-2020-16881)
- Windows (CVE-2020-1252)
- Windows Camera Codec Pack (CVE-2020-0997)
- Windows Media Audio Decoder (CVE-2020-1508, CVE-2020-1593)
- Windows Text Service Module (CVE-2020-0908)
 Denial of Service
Denial of Service
- Windows DNS (CVE-2020-0836, CVE-2020-1228)
- Windows Hyper-V (CVE-2020-0890, CVE-2020-0904)
- Windows Routing Utilities (CVE-2020-1038)
 Elevation of Privilege
Elevation of Privilege
- Connected User Experiences and Telemetry Service (CVE-2020-1590)
- Diagnostics Hub Standard Collector (CVE-2020-1130, CVE-2020-1133)
- DirectX (CVE-2020-1053)
- Group Policy (CVE-2020-1013)
- Microsoft COM for Windows (CVE-2020-1507)
- Microsoft Store Runtime (CVE-2020-0766, CVE-2020-1146)
- Microsoft splwow64 (CVE-2020-0790)
- NTFS (CVE-2020-0838)
- OneDrive for Windows (CVE-2020-16851, CVE-2020-16852, CVE-2020-16853)
- Shell infrastructure component (CVE-2020-0870)
- WinINet API (CVE-2020-1012)
- Windows (CVE-2020-1052, CVE-2020-1159, CVE-2020-1376)
- Windows CloudExperienceHost (CVE-2020-1471)
- Windows Cryptographic Catalog Services (CVE-2020-0782)
- Windows Function Discovery SSDP Provider (CVE-2020-0912)
- Windows Function Discovery Service (CVE-2020-1491)
- Windows Graphics Component (CVE-2020-0998)
- Windows InstallService (CVE-2020-1532)
- Windows Language Pack Installer (CVE-2020-1122)
- Windows Modules Installer (CVE-2020-0911)
- Windows Print Spooler (CVE-2020-1030)
- Windows RSoP Service Application (CVE-2020-0648)
- Windows Runtime (CVE-2020-1169, CVE-2020-1303)
- Windows Shell Infrastructure Component (CVE-2020-1098)
- Windows Start-Up Application (CVE-2020-1506)
- Windows Storage Services (CVE-2020-0886, CVE-2020-1559)
- Windows UPnP Service (CVE-2020-1598)
- Windows dnsrslvr.dll (CVE-2020-0839)
 Security Feature Bypass
Security Feature Bypass
- Microsoft ASP.NET Core (CVE-2020-1045)
- Projected Filesystem (CVE-2020-0805)
- SQL Server Reporting Services (CVE-2020-1044)
- Windows Defender Application Control (CVE-2020-0951)
 Information Disclosure
Information Disclosure
- Microsoft Excel (CVE-2020-1224)
- Microsoft Graphics Component (CVE-2020-0921, CVE-2020-1083)
- Microsoft Office (CVE-2020-16855)
- Microsoft splwow64 (CVE-2020-0875)
- Projected Filesystem (CVE-2020-16879)
- TLS (CVE-2020-1596)
- Windows (CVE-2020-1119)
- Windows DHCP Server (CVE-2020-1031)
- Windows GDI (CVE-2020-1256)
- Windows Graphics Component (CVE-2020-1091, CVE-2020-1097)
- Windows Mobile Device Management Diagnostics (CVE-2020-0989)
- Windows State Repository Service (CVE-2020-0914)
 Spoofing
Spoofing
- ADFS (CVE-2020-0837)
- Xamarin.Forms (CVE-2020-16873)
What vulnerabilities of other types do VM vendors mention in their report?
Denial of Service in Windows DNS (CVE-2020-0836, CVE-2020-1228). "In order to exploit this issue, an authenticated attacker would need to send a crafted, malicious DNS query to an affected host, resulting in an exhaustion of resources causing the device to become unresponsive."
Security Feature Bypass in Windows Defender Application Control (CVE-2020-0951). Comment from ZDI expert: "An attacker with administrative privileges on a local machine could connect to a PowerShell session and send commands to execute arbitrary code. However, what’s really interesting is that this is getting patched at all. Vulnerabilities that require administrative access to exploit typically do not get patches. I’m curious about what makes this one different."
8.8 High
CVSS3
Attack Vector
NETWORK
Attack Complexity
LOW
Privileges Required
NONE
User Interaction
REQUIRED
Scope
UNCHANGED
Confidentiality Impact
HIGH
Integrity Impact
HIGH
Availability Impact
HIGH
CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
9.3 High
CVSS2
Access Vector
NETWORK
Access Complexity
MEDIUM
Authentication
NONE
Confidentiality Impact
COMPLETE
Integrity Impact
COMPLETE
Availability Impact
COMPLETE
AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C